Nutrition, health and food security
As staple foods, maize and wheat provide vital nutrients and health benefits, making up close to two-thirds of the world’s food energy intake, and contributing 55 to 70 percent of the total calories in the diets of people living in developing countries, according to the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization. CIMMYT scientists tackle food insecurity through improved nutrient-rich, high-yielding varieties and sustainable agronomic practices, ensuring that those who most depend on agriculture have enough to make a living and feed their families. The U.N. projects that the global population will increase to more than 9 billion people by 2050, which means that the successes and failures of wheat and maize farmers will continue to have a crucial impact on food security. Findings by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, which show heat waves could occur more often and mean global surface temperatures could rise by up to 5 degrees Celsius throughout the century, indicate that increasing yield alone will be insufficient to meet future demand for food.
Achieving widespread food and nutritional security for the world’s poorest people is more complex than simply boosting production. Biofortification of maize and wheat helps increase the vitamins and minerals in these key crops. CIMMYT helps families grow and eat provitamin A enriched maize, zinc-enhanced maize and wheat varieties, and quality protein maize. CIMMYT also works on improving food health and safety, by reducing mycotoxin levels in the global food chain. Mycotoxins are produced by fungi that colonize in food crops, and cause health problems or even death in humans or animals. Worldwide, CIMMYT helps train food processors to reduce fungal contamination in maize, and promotes affordable technologies and training to detect mycotoxins and reduce exposure.
How collaboration can help grow and transform agriculture in Africa
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
Money alone can’t solve Africa’s agricultural problems. International collaboration is key.
Mexico and CIMMYT share a common vision for sustainable food production
 Capacity development
Capacity development
Mexico’s Secretariat of Agriculture, Livestock, Rural Development, Fisheries and Food (SAGARPA) is committed to provide Mexican farmers with the best possible seed and technical support, according to Baltazar Hinojosa Ochoa, Mexico’s secretary of agriculture, during his first visit to the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) on May 6.
Farmers in Ethiopia willing to pay more for quality protein maize
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
In Ethiopia, 44 percent of children under the age of five experience impaired growth due to poor nutrition. Quality protein maize helps combat stunting and boosts nutrition in children who survive on a maize-dominated diet.
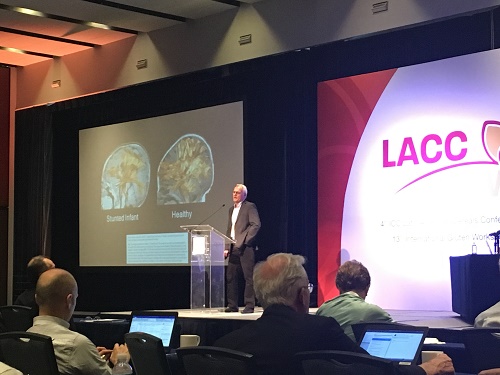
Global maize experts discuss biofortification for nutrition and health
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
At the 2018 Latin American Cereals Conference (LACC), researchers discussed hidden hunger, the consumption of insufficient micronutrients, and how biofortification can help.
Young women scientists who will galvanize global wheat research
 Capacity development
Capacity development
Winners of the Jeanie Borlaug Laube Women in Triticum (WIT) Early Career Award joined an on-going wheat research training course organized by CIMMYT.
Scientists seek key to boost yields, ensure future food supply
 Climate adaptation and mitigation
Climate adaptation and mitigation
Crop genetic gains remain too low, and international scientists are making a concerted effort to determine how best to increase yields.
Field trial design workshop for smallholder farmers who grow maize landraces
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
As part of the efforts of the Sustainable Modernization of Traditional Agriculture program aimed at improving food security based on maize landraces in marginal areas of the state of Oaxaca, Mexico
Global grain research and food industry experts meet to address rising malnutrition
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
Malnutrition is rising again and becoming more complex, according to the director-general of the world’s leading public maize and wheat research center.
First zinc maize variety launched to reduce malnutrition in Colombia
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
A new zinc-enriched maize variety developed by CIMMYT was released in Colombia to help combat malnutrition in South America.
Scientists confirm value of whole grains and wheat for nutrition and health
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
New Publications: Storage of maize products results in vitamin loss
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
Deadly strain of wheat stem rust disease surfaces in Europe
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
Scientists have shown that the first appearance of wheat stem rust disease in the U.K. in nearly 60 years, which occurred in 2013, was caused by the same virulent fungal strain responsible for recent wheat stem rust outbreaks in Ethiopia, Denmark, Germany, and Sweden.