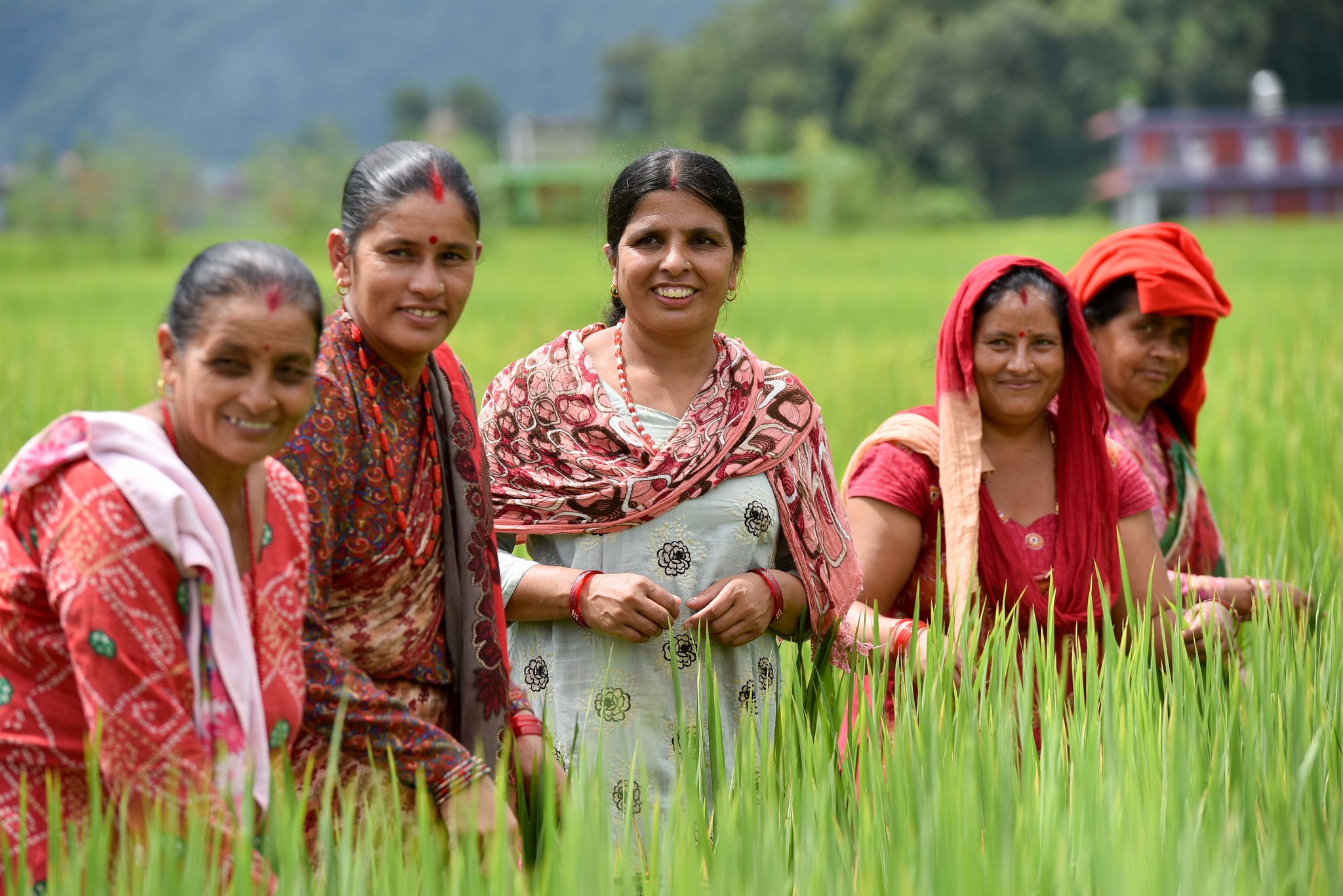
GENNOVATE is a global comparative research initiative which addresses the question of how gender norms influence men, women and youth to adopt innovation in agriculture and natural resource management.
Carried out in conjunction with 11 CGIAR research programs worldwide and across 125 rural communities in 26 countries, this qualitative comparative study aims to provide authoritative research to advance gender-transformative approaches and catalyze change in international agricultural and natural resource management research for development.
In discussion groups and individual interviews, roughly 6,000 rural study participants of different socioeconomic backgrounds and age groups are reflecting on and comparing local women’s and men’s expected roles and behaviors — or gender norms— and how these social rules affect their ability to access, adopt, adapt and benefit from innovations in agricultural and natural resource management.
The initiative’s research process strives to give rural women and men a voice by providing authoritative, contextually grounded evidence on how gender interacts with agricultural innovations. It also aims to strengthen CGIAR research program capacities to know the target beneficiaries, design for them, and be accountable to them.
Central to the qualitative field study is an exploration of women’s and men’s agency at the core of which is the capacity to make important decisions pertaining to one’s life. For rural women and men, these decisions relate to agriculture and natural resource management, as well as to other significant events in the private (household) and public (community) spheres.
OBJECTIVES
- What are the most important new agricultural practices and technologies for the men and for the women in a given village?
- What qualities make a woman or a man a good farmer?
- Do young people in this village follow local customs of women doing certain agricultural activities and men others?
- Are there differences between a woman who is innovative and a man who is innovative?


 Gender equality, youth and social inclusion
Gender equality, youth and social inclusion