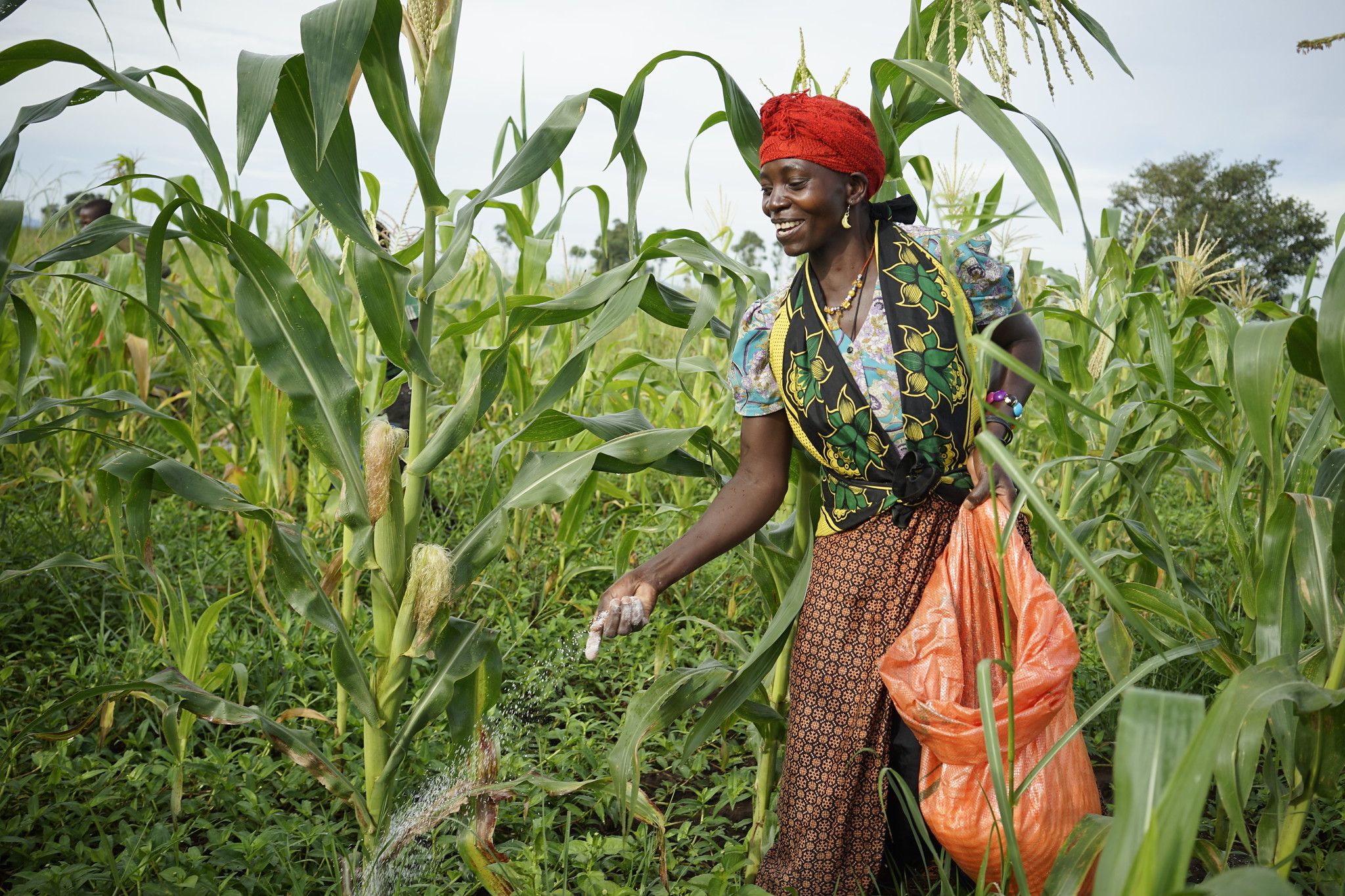
Given the very heterogeneous conditions in smallholder agriculture in sub-Saharan Africa, there is a growing policy interest in site-specific extension advice and the use of related digital tools. However, empirical ex ante studies on the design of this type of tools are scant and little is known about their impact on site-specific extension advice.
In partnership with Oyakhilomen Oyinbo and colleagues at KU Leuven, scientists at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) have carried out research to clarify user preferences for tailored nutrient management advice and decision-support tools. The studies also evaluated the impact of targeted fertilizer recommendations enabled by such tools.
Understanding farmers’ adoption
A better understanding of farmers’ and extension agents’ preferences may help to optimize the design of digital decision-support tools.
Oyinbo and co-authors conducted a study among 792 farming households in northern Nigeria, to examine farmers’ preferences for maize intensification in the context of site-specific extension advice using digital tools.
Overall, farmers were favorably disposed to switch from general fertilizer use recommendations to targeted nutrient management recommendations for maize intensification enabled by decision-support tools. This lends credence to the inclusion of digital tools in agricultural extension. The study also showed that farmers have heterogeneous preferences for targeted fertilizer recommendations, depending on their resources, sensitivity to risk and access to services.
The authors identified two groups of farmers with different preference patterns: a first group described as “strong potential adopters of site-specific extension recommendations for more intensified maize production” and a second group as “weak potential adopters.” While the two groups of farmers are willing to accept some yield variability for a higher average yield, the trade-off is on average larger for the first group, who have more resources and are less sensitive to risk.
The author recommended that decision-support tools include information on the riskiness of expected investment returns and flexibility in switching between low- and high-risk recommendations. This design improvement will help farmers to make better informed decisions.
Extension agents go digital
While farmers are the ultimate recipients of extension advice, extension agents are most often the actual users of decision-support tools. In another study, the authors provided ex ante insights on the potential uptake of nutrient management decision-support tools and the specific design features that are more (or less) appealing to extension agents in the maize belt of northern Nigeria.
Using data from a discrete choice experiment, the study showed that extension agents were generally willing to accept the use of digital decision-support tools for site‐specific fertilizer recommendations. While extension agents in the sample preferred tools with a more user‐friendly interface that required less time to generate an output, the authors also found substantial preference heterogeneity for other design features. Some extension agents cared more about the outputs, such as information accuracy and level of detail, while others prioritized practical features such as the tool’s platform, language or interface.
According to the authors, accounting for such variety of preferences into the design of decision-support tools may facilitate their adoption by extension agents and, in turn, enhance their impact in farmars’ agricultural production decisions.
Impact of digital tools
Traditional extension systems in sub-Saharan African countries, including Nigeria, often provide general fertilizer use recommendations which do not account for the substantial variation in production conditions. Such blanket recommendations are typically accompanied by point estimates of expected agronomic responses and associated economic returns, but they do not provide any information on the variability of the expected returns associated with output price risk.
Policymakers need a better understanding of how new digital agronomy tools for tailored recommendations affect the performance of smallholder farms in developing countries.
To contribute to the nascent empirical literature on this topic, Oyinbo and colleagues evaluated the impact of a nutrient management decision-support tool for maize – Nutrient Expert — on fertilizer use, management practices, yields and net revenues. The authors also evaluated the impacts of providing information about variability in expected investment returns.
To provide rigorous evidence, the authors conducted a three-year randomized controlled trial among 792 maize-producing households in northern Nigeria. The trial included two treatment groups who are exposed to site-specific fertilizer recommendations through decision-support tools — one with and another one without additional information on variability in expected returns — and a control group who received general fertilizer use recommendations.
Overall, the use of nutrient management decision-support tools resulted in greater fertilizer investments and better grain yields compared with controls. Maize grain yield increased by 19% and net revenue increased by 14% after two years of the interventions. Fertilizer investments only increased significantly among the farmers who received additional information on the variability in expected investment returns.
The findings suggest including site-specific decision support tools into extension programming and related policy interventions has potential benefits on maize yields and food security, particularly when such tools also supply information on the distribution of expected returns to given investment recommendations.
The research-for-development community has tried different approaches to optimize fertilizer recommendations. In Nigeria, there are several tools available to generate location-specific fertilizer recommendations, including Nutrient Expert. As part of the Taking Maize Agronomy to Scale in Africa (TAMASA) project, CIMMYT has been working on locally calibrated versions of this tool for maize farmers in Ethiopia, Nigeria and Tanzania. The development was led by a project team incorporating scientists from the African Plant Nutrition Institute (APNI), CIMMYT and local development partners in each country.
Next steps
Some studies have shown that dis-adoption of seemingly profitable technologies — such as fertilizer in sub-Saharan Africa — is quite common, especially when initial returns fall short of expectations or net utility is negative, producing a disappointment effect.
In the context of emerging digital decision-support tools for well-targeted fertilizer use recommendations, it remains unclear whether farmers’ initial input use responses and the associated economic returns affect their subsequent responses — and whether the disappointment effect can be attenuated through provision of information about uncertainty in expected returns.
Using our three-year randomized controlled trial and the associated panel dataset, researchers are now working on documenting the third-year responses of farmers to site-specific agronomic advice conditional on the second-year responses. Specifically, they seek to better document whether providing farmers with information about seasonal variability in expected investment returns can reduce possible disappointment effects associated with their initial uptake of site-specific agronomic advice and, in a way, limit dis-adoption of fertilizer.
Cover photo: A farmer shows maize growing in his field, in one of the communities in northern Nigeria where research took place. (Photo: Oyakhilomen Oyinbo)




 Innovations
Innovations 
