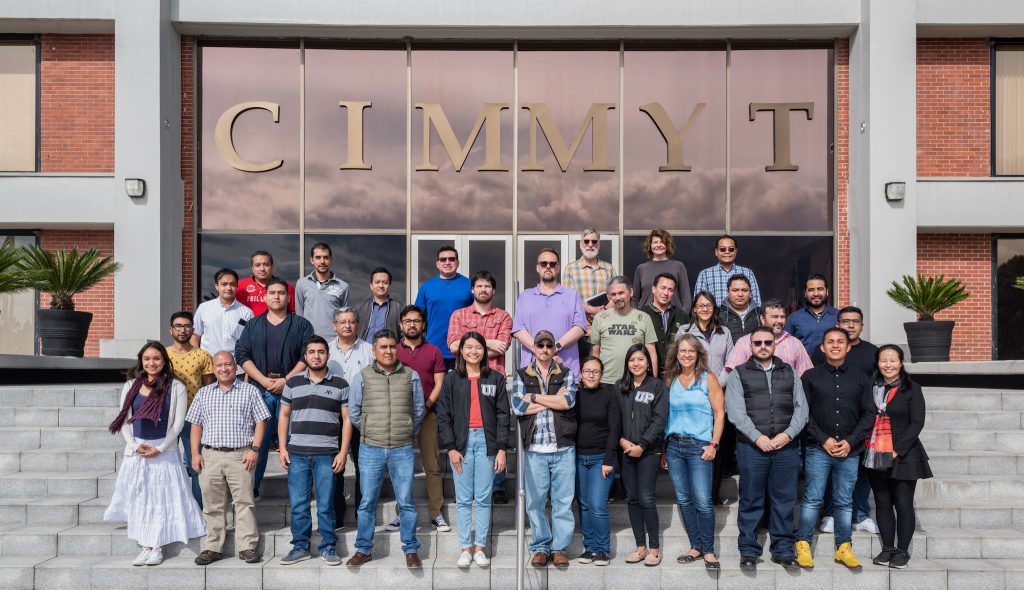
From October 21 to November 1, 2019, software developers and administrators from several breeding software projects met at the global headquarters of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) in Mexico to work on delivering an integrated solution to crop breeders.
Efforts to improve crop breeding for lower- and middle-income countries involves delivering better varieties to farmers faster and for less cost. These efforts rely on a mastery of data and technology throughout the breeding process.
To realize this potential, the CGIAR Excellence in Breeding Platform (EiB) is developing an Enterprise Breeding System (EBS) as a single solution for breeders. EBS will integrate the disparate software projects developed by different institutions over the years. This will free breeders from the onerous task of managing their data through different apps and allow them to rapidly optimize their breeding schemes based on sound data and advanced analytics.
“None of us can do everything,” said Tom Hagen, CIMMYT-EiB breeding software product manager, “so what breeding programs are experiencing is in fact fragmented IT. How do we come together as IT experts to create a system through our collective efforts?”
For the EBS to succeed, it is essential that the system is both low-cost and easy to deploy. “The cost of the operating environment is absolutely key,” said Jens Riis-Jacobson, international systems and IT director at CIMMYT. “We are trying to serve developing country institutions that have very little hard currency to pay for breeding program operations.”
Stacked software
During the hackathon, twelve experts from software projects across CGIAR and public sector institutions used a technology called Docker to automatically stack the latest versions of their applications into a single configuration file. This file can be loaded into any operating environment in less than four minutes — whether it be a laptop, local server or in the cloud. Quickly loading the complete system into a cloud environment means EBS can eventually be available as a one-click, Software-as-a-Service solution. This means that institutions will not need sophisticated IT infrastructure or support staff to maintain the software.
“If everything goes as planned, the end users won’t know that we exist,” said Peter Selby, coordinator of the Breeding API (BrAPI) project, an online collective working on a common language for breeding applications to communicate with each other. Updates to individual apps will be automatically loaded, tested and pushed out to users.
As well as the benefits to breeders, this automated deployment pipeline should also result in better software. “We have too little time for development because we spend too much time in deployment and testing,” said Riis-Jacobson.
A cross-institution DevOps culture
Though important technical obstacles were overcome, the cultural aspect was perhaps the most significant outcome of the hackathon. The participants found that they shared the same goals, language and were able to define the common operating environment for their apps to work together in.
“It’s really important to keep the collaboration open,” said Roy Petrie, DevOps engineer at the Genomic and Open-Source Breeding Informatics Initiative (GOBii) based at the Boyce Thompson Institute, Cornell University. “Having a communications platform was the first thing.”
In the future, this could mean that teams synchronize their development timeline to consistently release updates with new versions of the EBS, suggested Franjel Consolacion, systems admin at CIMMYT.
“They are the next generation,” remarked Hagen. “This is the first time that this has happened in CGIAR informatics and it validated a key aspect of our strategy: that we can work together to assemble parts of a system and then deploy it as needed to different institutions.”
By early 2020, selected CIMMYT and International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) breeding teams will have access to a “minimal viable implementation” of the EBS, in which they can conduct all basic breeding tasks through a simple user interface. More functionality, breeding programs and crops from other institutions including national agricultural research programs will be added in phases over three years.

 Innovations
Innovations 
