Agrifood systems contribute to at least 12 of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). To advance these goals, agrifood systems need to deliver more nutritious food to more people and simultaneously be environmentally sustainable and resilient. Changes are required at multiple levels to include more sustainable farming, reduce food losses in distribution and retail, and increase the intake of healthier foods by consumers.
Recent studies show that piecemeal interventions focusing on only one aspect or area are insufficient to make the required transformation. Issues related to food security and improved nutrition are complex, and their solutions must transcend traditional disciplinary and institutional boundaries.
Agrifood systems research looks to understand how systems work and actions by governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and the private sector that can positively influence outcomes at scale. Researchers and development professionals use this approach to assess how different actors, practices and policies share the production, marketing, availability, and consumption of food. Agriculture, trade, policy, health, environment, transport, infrastructure, gender norms and education all have a role to play in achieving resilient agrifood systems that deliver greater benefits to farmers and consumers.
CIMMYT combines the expertise of economists, agronomists, crop breeders, nutritionists, and gender specialist to create more sustainable, nutritious, and profitable agrifood systems in multiple ways. It works to ensure that cereal crops are grown in the most sustainable way, that the public and private sectors are informed about consumer preferences, and that quality improved seed is available to farmers when they need it. CIMMYT also aims to better understand how cereal based foods are processed and sold to consumers and develop options for promoting the consumption of more nutritious cereal-based foods.
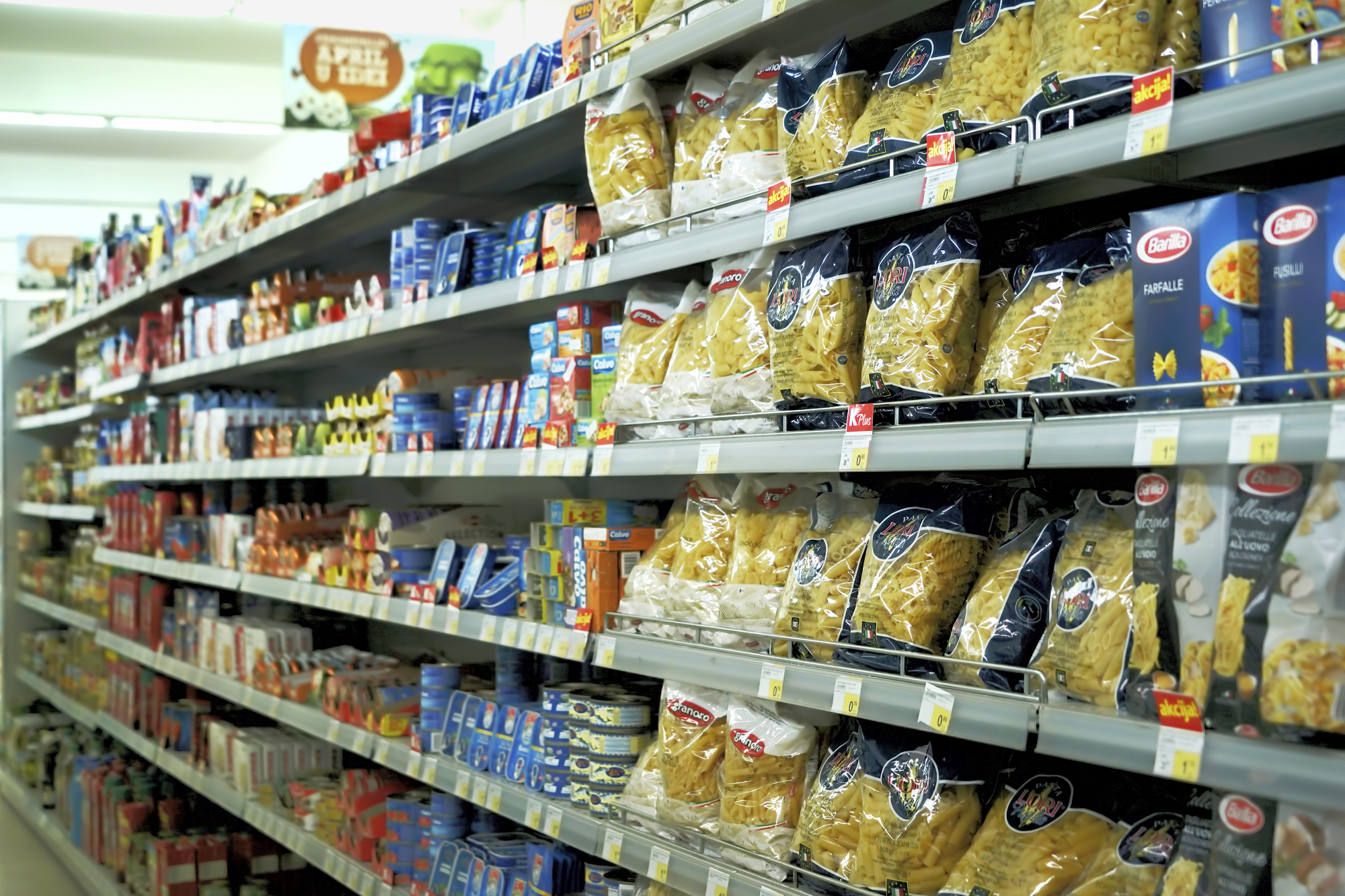

Consumer demand in Mexico
Recently, CIMMYT partnered with the National Institute of Public Health of Mexico (INSP), to compare access to healthy processed cereal-based food in supermarkets, convenience stores, and corner stores for consumers from low- and high-income neighborhoods in Mexico City. Discussions continue to rage about how policies can support more nutritious and healthier diets in Mexico, including the new requirement for food warning labels on the front of packaging.
The study showed that availability of healthy products was scarce in most stores, particularly in convenience stores. Compared to supermarkets in the low-income areas, those in high-income areas exhibited a greater variety of healthy products across all categories. A follow up study is underway that examines the outcomes of the new food label warnings on product availability and health claims.
Other CIMMYT studies have explored the demand by lower- and middle-income consumers in central Mexico for healthy cereal-based foods, including their demand for blue maize tortillas and whole grain bread. These studies help policy makers and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) design strategies on how to increase access and consumption of healthier processed wheat and maize products in fast-evolving food systems.
Blending wheat products in Kenya
In many parts of the world, the Ukraine-Russia war has intensified the need to change how wheat-based products are formulated. For example, Kenya is a country where wheat consumption has been growing rapidly for a decade, yet imports have comprised 90% of its wheat supplies, which up until recently came from Ukraine and Russia. Wheat flour blending in Kenya is a promising option for reducing wheat imports, generating demand for other, lesser-utilized cereals, such as sorghum, and increasing the nutrient profile of bread products. But wheat blending, despite having been discussed for many years in Kenya, has yet to gain traction.
In response, CIMMYT and the Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology (JKUAT) are exploring the feasibility of reducing wheat imports in Kenya by replacing between 5-20% of wheat flour with flour derived from other cereals, including sorghum and millet. While existing evidence suggests that consumers may except up to 10% blending in cereal flours, the stakes are high for both the wheat industry and government. Robust and context specific evidence is needed on consumers’ willingness to accept blended products in urban Kenya and the economic feasibility of blending from the perspective of millers and processors.
Among the critical questions to be explored by CIMMYT and JKUAT: What flour blends will consumers most likely to accept? What are the potential health benefits from blending with sorghum and millet? Is there enough sorghum and millet readily available to replace the wheat removed from flour? And finally, what is the business case for wheat flour blending?
Cover photo: Wheat harvest near Iztaccíhuatl volcano in Juchitepec, Estado de México. (Photo: CIMMYT/ Peter Lowe)


 Climate adaptation and mitigation
Climate adaptation and mitigation 
