The International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (IWGSC) is pleased to announce that the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), has joined the organization as a sponsoring partner.
The IWGSC is an international, collaborative consortium of wheat growers, plant scientists, and public and private breeders dedicated to the development of genomic resources for wheat scientists and breeders to facilitate the production of wheat varieties better adapted to today’s challenges – climate change, food security and biodiversity preservation. In 2018, the IWGSC published the first genome reference sequence of the bread wheat, an essential tool to identify more rapidly genes and regulatory elements underlying complex agronomic traits such as yield, grain quality, resistance to diseases, and tolerance to stress such as drought or salinity.
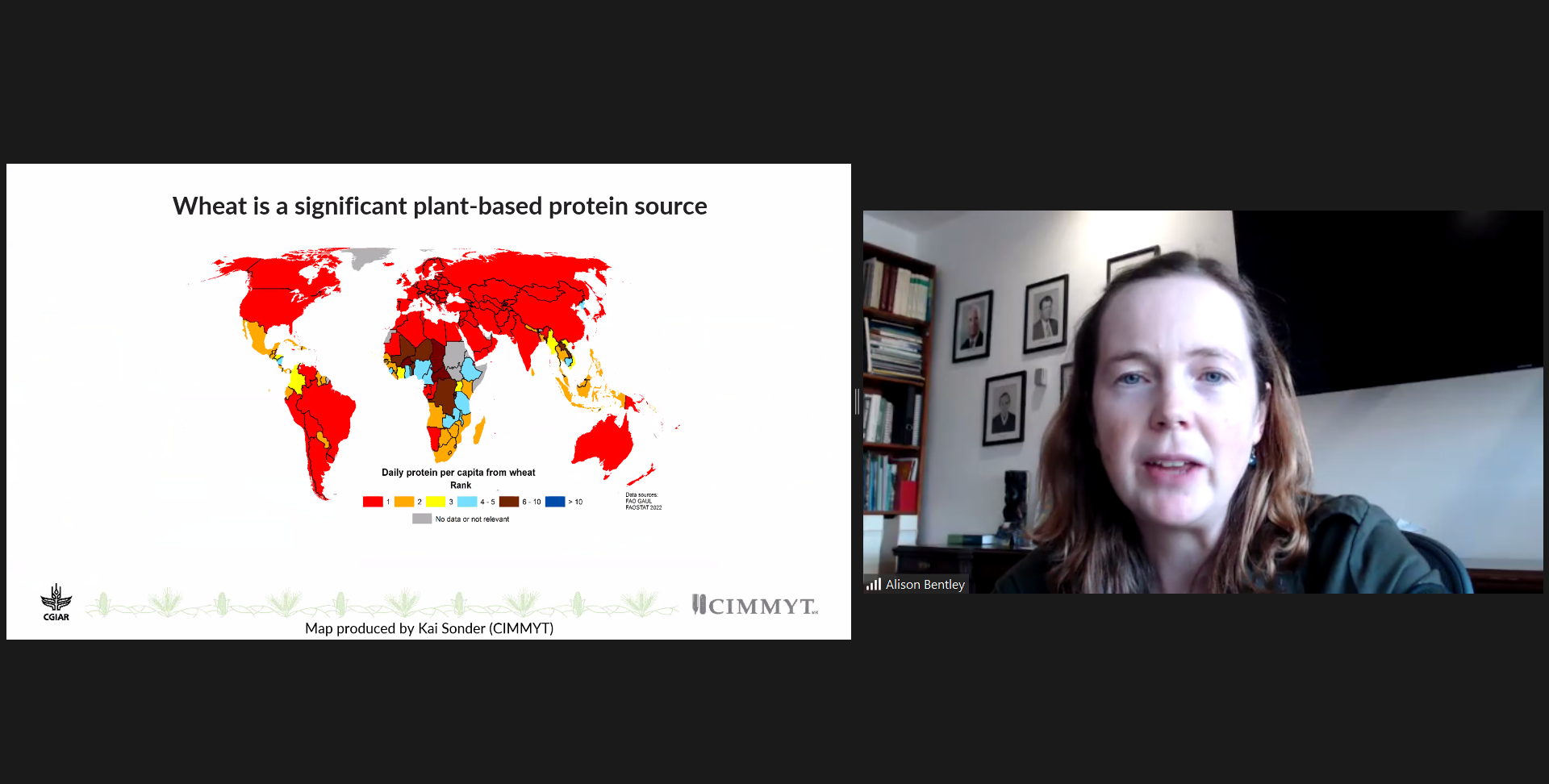
The International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center, known by its Spanish acronym, CIMMYT, is a non-profit international agricultural research and training organization focusing on two of the world’s most important cereal grains: maize and wheat, and related cropping systems and livelihoods. CIMMYT’s maize and wheat research addresses challenges encountered by low-income farmers in the developing world including food and nutritional insecurity, environmental degradation, economic development, population growth and climate change.
CIMMYT’s Global Wheat Program is one of the most important public sources of high yielding, nutritious, disease- and climate-resilient wheat varieties for Africa, Asia, and Latin America. CIMMYT breeding lines can be found in varieties sown on more than 60 million hectares worldwide.
“I am truly pleased that CIMMYT has re-joined the IWGSC. The current reference sequences have been absolutely essential, enabling us to design new trait-based markers for use in CIMMYT wheat breeding pipelines. There remains much to explore in characterizing wheat at the whole genome level,” said CIMMYT wheat molecular breeding laboratory lead, Susanne Dreisigacker.
Sponsors are an essential part of the IWGSC. They participate in IWGSC-led projects and, as members of the Coordinating Committee, they help shape the IWGSC priorities, strategic plans, and activities. Susanne Dreisigacker will represent CIMMYT in the IWGSC Coordinating Committee.
“CIMMYT is a leading force in developing wheat varieties for southern countries,” said Kellye Eversole, Executive Director of the IWGSC. “We are thrilled that they are joining forces with the IWGSC to build the genomic tools and resources that will ensure growers around the world have access to resilient and highly productive wheat varieties.”
After release of the wheat genome reference sequence in 2018, the IWGSC entered Phase II with activities focused on developing tools to accelerate the development of improved varieties and to empower all aspects of basic and applied wheat science. The organization recently released versions 2.1 of the reference sequence assembly and annotation, and is continuing to work with the wheat community to improve the reference sequence by gap filling and integration of manual and functional annotation. The IWGSC also is focused on securing funding for a project that will ensure that “platinum-quality” sequences, representing the worldwide wheat diversity of landraces and elite varieties, are available publicly for breeders.
About the International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium
The IWGSC, with 3,300 members in 71 countries, is an international, collaborative consortium, established in 2005 by a group of wheat growers, plant scientists, and public and private breeders. The goal of the IWGSC is to make a high-quality genome sequence of bread wheat publicly available, in order to lay a foundation for basic research that will enable breeders to develop improved varieties. The IWGSC is a U.S. 501(c)(3) non-profit organization. To learn more, visit www.wheatgenome.org and follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn and YouTube.
 Climate adaptation and mitigation
Climate adaptation and mitigation 
