The 2023 UN Climate Change Conference (COP 28) took place from November 30 to December 12, 2023, in Dubai, UAE. The conference arrived at a critical moment when over 600 million people face chronic hunger, and global temperatures continue to rise at alarming rates. CIMMYT researchers advocated for action into agriculture’s mitigating role in climate change, increasing crop diversity, and bringing the tenets of sustainability and regenerative agroecological production systems to a greater number of farmers.
Directly addressing the needs of farmers, CIMMYT proposed the creation of an advanced data management system, training, and protocols for spreading extension innovations such as digital approaches and agronomic recommendations to farmers via handheld devices to harmonize the scaling in Africa of regenerative agriculture—diverse practices whose outcomes include better productivity and environmental quality, economic feasibility, social inclusivity, and nutritional security.
CIMMYT presented research showing that in times of fertilizer shortages, targeting nitrogen supplies from inorganic and organic sources to farms with minimal access to nitrogen inputs can improve nitrogen-use efficiency and helps maintain crop yields while limiting harm from excesses in fertilizer use. Examining how food production is driving climate change, CIMMYT promoted ways to lessen climate shocks, especially for smallholder farmers who inordinately suffer the effects of climate change, including rising temperatures and extended droughts. Improved, climate-resilient crop varieties constitute a key adaptation. Boosting farmer productivity and profits is a vital part of improving rural livelihoods in Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
When asked about CIMMYT’s contribution to COP 28, Bram Govaerts, CIMMYT’s director general, highlighted the inclusion of agriculture in the COP28 UAE Declaration on Sustainable Agriculture, Resilient Food Systems, and Climate Action as part of various potential solutions for climate change, an effort that CIMMYT supported through advocacy with leaders and government officials.
“Our participation addressed some of the pressure points which led to this significant recognition. It further cleared our role as an active contributor to discussions surrounding the future of food and crop science,” said Govaerts.
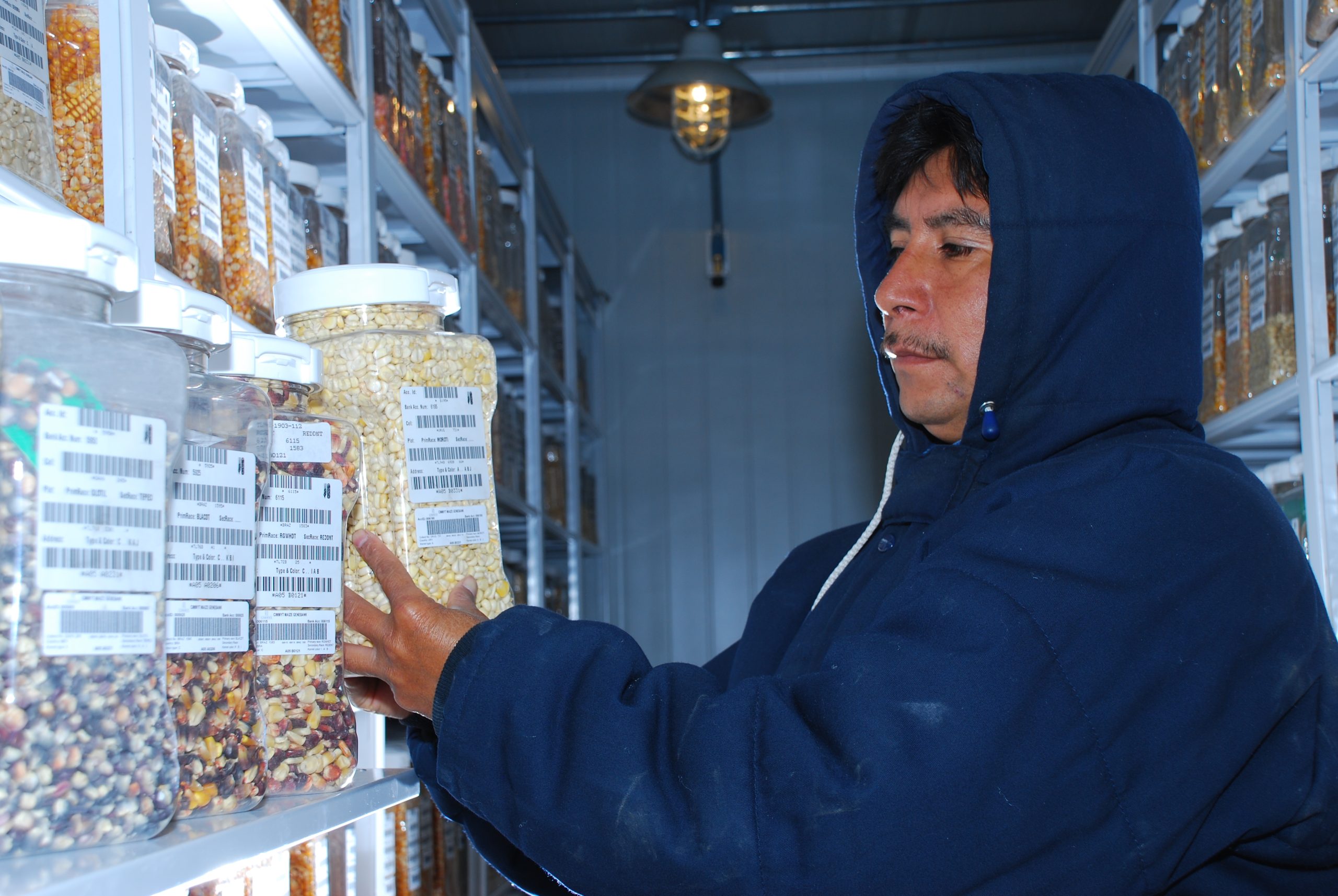
Unlocking the potential of crop genetic diversity
“The diversity stored in today’s gene banks contains the potential to unlock genes that can withstand drought and warmer temperatures,” said Sarah Hearne, CIMMYT’s director of Genetic Resources at a side-event: Crop diversity for climate change adaptation and mitigation contributing to resilient and nature positive futures for farmers globally.

Hearne explained the process that characterizes plant DNA to identify the ideal, climate-adaptable breeding traits. This classification system also opens the door for genetic modeling, which can predict key traits for tomorrow’s climatic and environmental conditions.
“Our thinking must shift from thinking of gene banks to banks of genes, to make vibrant genetic collections for humanity, opening up genetic insurance for farmers,” said Hearne.
Working towards a food system that works for the environment
With an increased strain on food production, sustainability becomes critical for long-term human and environmental health. Sarah Hearne and Tek Sapkota, agricultural systems and climate change senior scientist, from CIMMYT participated in a panel discussion: Responsible consumption and sustainable production: pathways for climate-friendly food systems. They shared how progress in genetic innovation and fertilizer use can contribute to sustainable consumption and a resilient food system.
Fertilizer use remains highly skewed, with some regions applying more fertilizer than required and others, like sub-Saharan Africa, not having sufficient access, resulting in low crop yields. However, to achieve greater food security, the Global South must produce more food. For that, they need to use more fertilizer. Just because increased fertilizer use will increase greenhouse gases (GHGs) emissions, institutions cannot ask smallholder farmers not to increase fertilizer application. Increased GHGs emission with additional fertilizer application in low-input areas can be counterbalanced by improving Nutrient-Use Efficiency (NUE) in high-output areas thereby decreasing GHGs emissions. This way, we can increase global food production by 30% ca with the current level of fertilizer consumption.

“This issue needs to be considered through a holistic lens. We need to scale-up already proven technologies using digital extensions and living labs and linking farmers with markets,” said Sapkota.
On breeding climate-resilient seeds, Hearne addressed whether farmers are accepting new seeds and how to ensure their maximum adoption. Hearne detailed the partnership with CGIAR and NARS and the numerous technologies advancing the selection of ideal breeding traits, considering shortened breeding cycles, and responding to local needs such as heat or flood tolerance, and traditional preferences.
“Drought-tolerant maize, developed by CIMMYT and the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA), has benefited over 8 million households in sub-Saharan Africa, which proves that farmers are increasingly receptive to improved seeds. With a better selection of appropriate traits, we can further develop and distribute without yield penalties,” said Hearne.
Regenerative and agroecological production systems
Researchers have studied regenerative and agroecological production systems for decades, with new and old research informing current debates. These systems restore and maintain ecosystems, improving resource use efficiency, strengthening resilience, and increasing self-sufficiency. In his keynote presentation, Sapkota presented 3 examples of regenerative agriculture and agroecological systems: conservation agriculture, cropping system diversification and site-specific nutrient management and their impact on food production, climate change adaptation and mitigation.
“As the science continues to develop, we need to harness digital capacity to co-create sustainable solutions alongside local, indigenous knowledge,” said Sapkota. “While we should continue research and innovation on cutting-edge science and technologies, we should also invest in knowledge sharing networks to spread access to this research; communication is fundamental for further adoption of these practices.”
 Climate adaptation and mitigation
Climate adaptation and mitigation 
