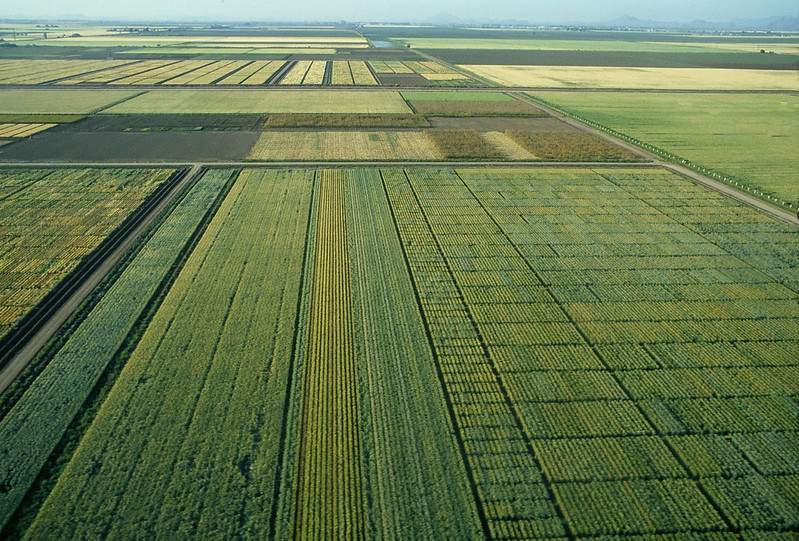
A collaboration involving 15 international institutes across eight countries has optimized efforts to introduce beneficial traits from wild wheat accessions in genebanks into existing wheat varieties.
The findings, published in Nature Food, extend many potential benefits to national breeding programs, including improved wheat varieties better equipped to thrive in changing environmental conditions. This research was led by Sukhwinder Singh of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) as part of the Seeds of Discovery project.
Since the advent of modern crop improvement practices, there has been a bottleneck of genetic diversity, because many national wheat breeding programs use the same varieties in their crossing program as their “elite” source. This practice decreases genetic diversity, putting more areas of wheat at risk to pathogens and environmental stressors, now being exacerbated by a changing climate. As the global population grows, shocks to the world’s wheat supply result in more widespread dire consequences.
The research team hypothesized that many wheat accessions in genebanks — groups of related plant material from a single species collected at one time from a specific location — feature useful traits for national breeding programs to employ in their efforts to diversify their breeding programs.
“Genebanks hold many diverse accessions of wheat landraces and wild species with beneficial traits, but until recently the entire scope of diversity has never been explored and thousands of accessions have been sitting on the shelves. Our research targets beneficial traits in these varieties through genome mapping and then we can deliver them to breeding programs around the world,” Singh said.
Currently adopted approaches to introduce external beneficial genes into breeding programs’ elite cultivars take a substantial amount of time and money. “Breeding wheat from a national perspective is a race against pathogens and other abiotic threats,” said Deepmala Sehgal, co-author and wheat geneticist in the Global Wheat program at CIMMYT. “Any decrease in the time to test and release a variety has a huge positive impact on breeding programs.”
Taking into genetic biodiversity
The findings build from research undertaken through the Seeds of Discovery project, which genetically characterized nearly 80,000 samples of wheat from the seed banks of CIMMYT and the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
First, the team undertook a large meta-survey of genetic resources from wild wheat varieties held in genebanks to create a catalog of improved traits.
“Our genetic mapping,” Singh said, “identifies beneficial traits so breeding programs don’t have to go looking through the proverbial needle in the haystack. Because of the collaborative effort of the research team, we could examine a far greater number of genomes than a single breeding program could.”
Next, the team developed a strategic three-way crossing method among 366 genebank accessions and the best historical elite varieties to reduce the time between the original introduction and deployment of an improved variety.
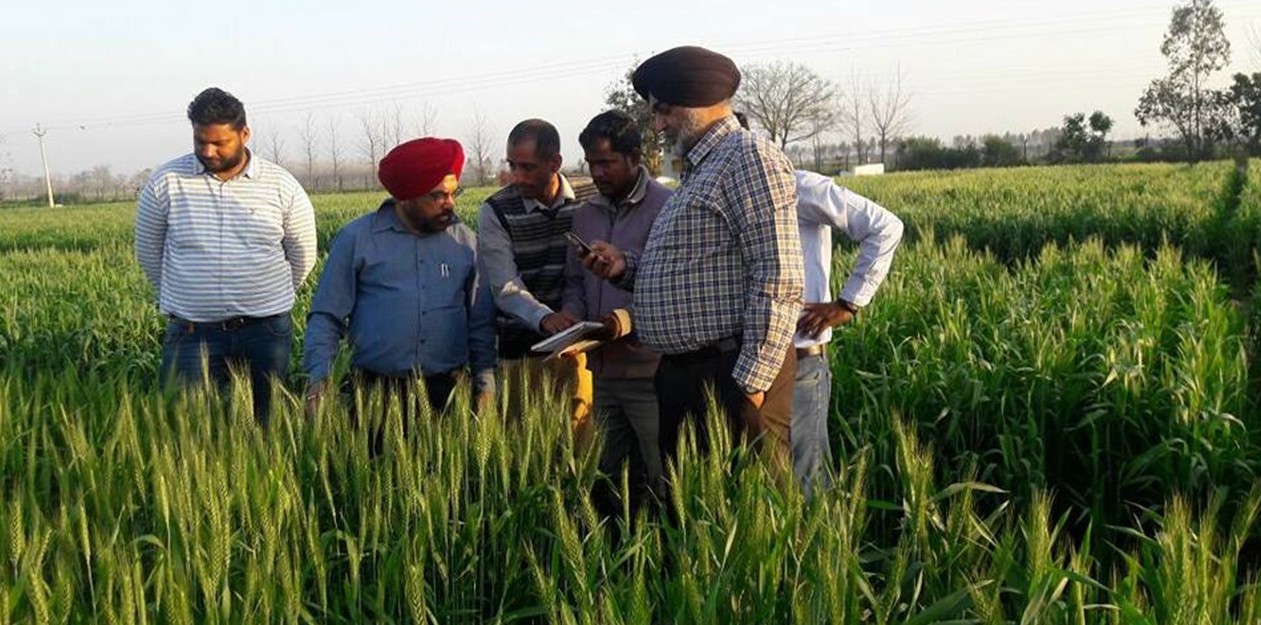

Worldwide impact
National breeding programs can use the diverse array of germplasm for making new crosses or can evaluate the germplasm in yield trials in their own environments.
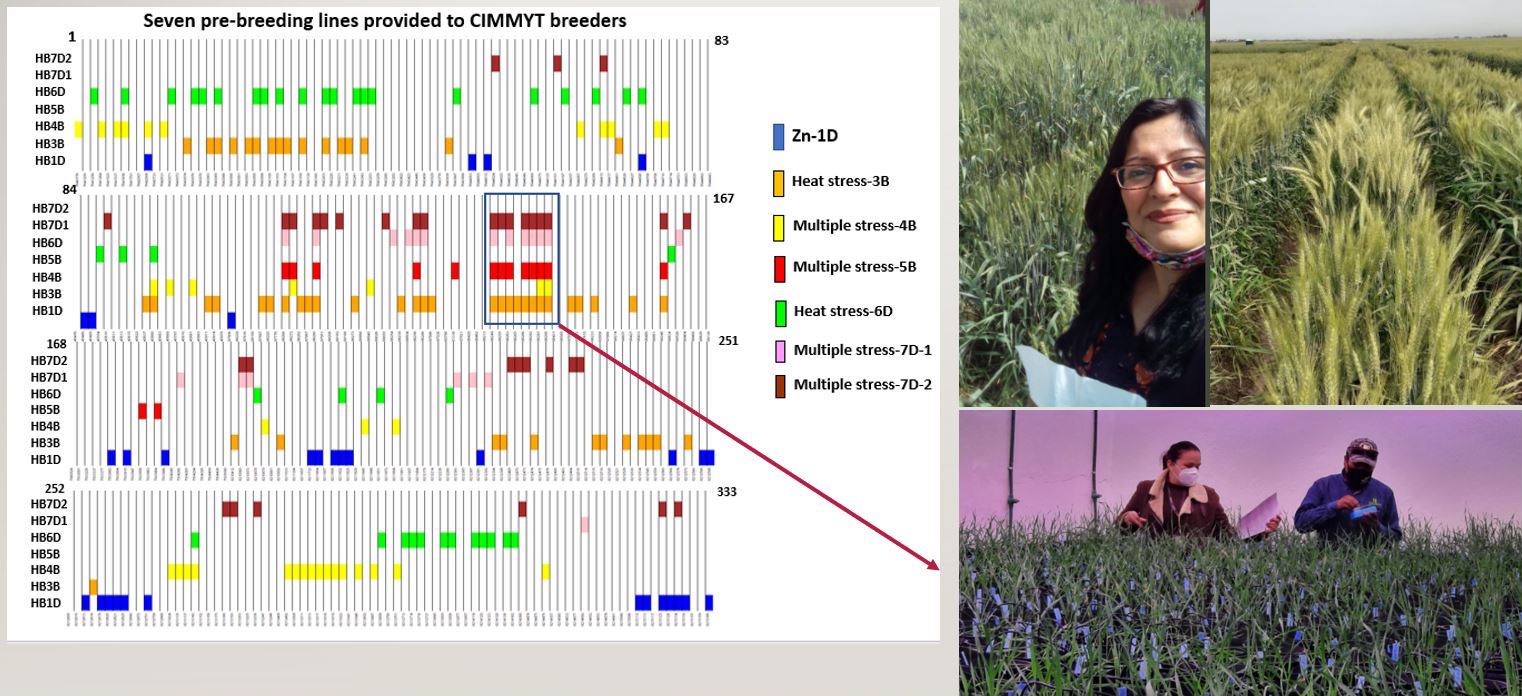
The diverse new germplasm is being tested in major wheat producing areas, including India, Kenya, Mexico and Pakistan. In Mexico, many of the lines showed increased resistance to abiotic stresses; many lines tested in Pakistan exhibited increased disease resistance; and in India, many tested lines are now part of the national cultivar release system. Overall, national breeding programs have adopted 95 lines for their targeted breeding programs and seven lines are currently undergoing varietal trials.
“This is the first effort of its kind where large-scale pre-breeding efforts have not only enhanced the understanding of exotic genome footprints in bread wheat but also provided practical solutions to breeders,” Sehgal said. “This work has also delivered pre-breeding lines to trait pipelines within national breeding programs.”
Currently, many of these lines are being used in trait pipelines at CIMMYT to introduce these novel genomic regions into advanced elite lines. Researchers are collaborating with physiologists in CIMMYT’s global wheat program to dissect any underlying physiological mechanisms associated with the research team’s findings.
“Our investigation is a major leap forward in bringing genebank variation to the national breeding programs,” Singh explained. “Most significantly, this study sheds light on the importance of international collaborations to bring out successful products and new methods and knowledge to identify useful contributions of exotic in elite lines.”
Read the full article:
Direct introgression of untapped diversity into elite wheat lines
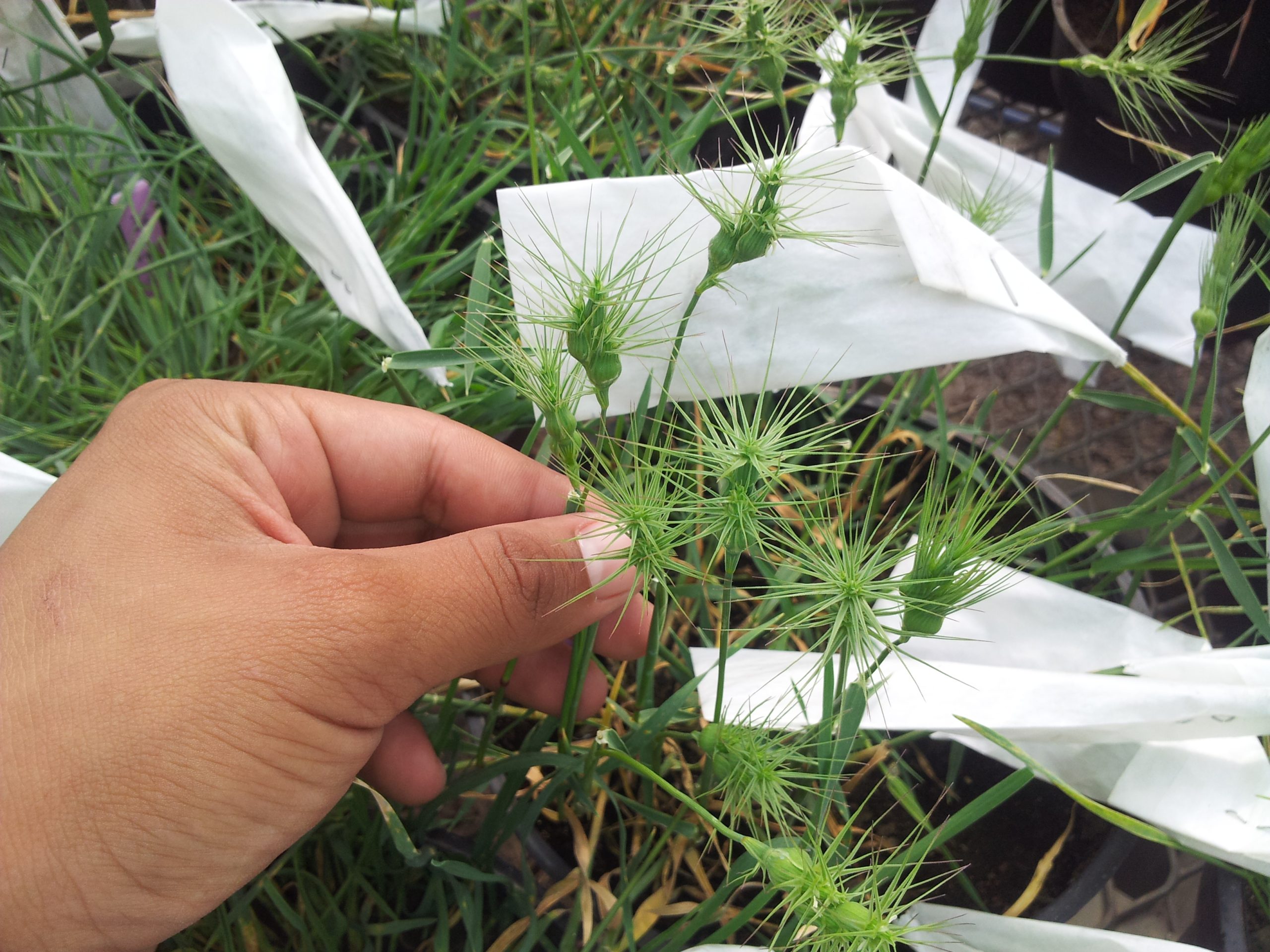
Cover photo: A researcher holds a plant of Aegilops neglecta, a wild wheat relative. Approximately every 20 years, CIMMYT regenerates wheat wild relatives in greenhouses, to have enough healthy and viable seed for distribution when necessary. (Photo: Rocío Quiroz/CIMMYT)


 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security 
