By Brenna Goth/CIMMYT
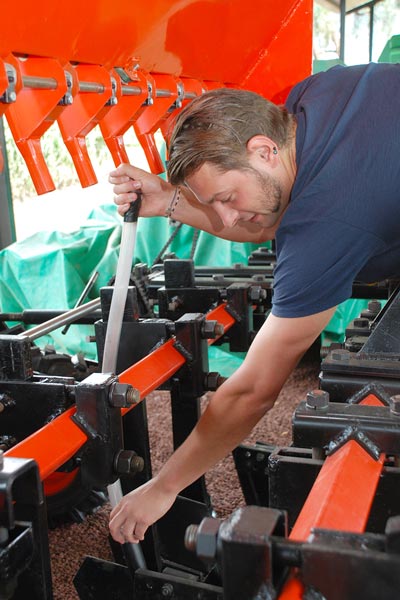

team is working to develop less expensive and more precise options. Photo: Xochiquetzal Fonseca/CIMMYT
Jelle Van Loon’s workshop in the fields at El Batán is all about experimentation. The CIMMYT engineer from Belgium is making affordable and efficient tools for smallholder farmers in Mexico by innovating technology and adapting what is already available. Van Loon, leader of smart mechanization for the conservation agriculture program in Mexico, works within the Take it to the Farmer component of MasAgro, or the Sustainable Modernization of Traditional Agriculture. MasAgro focuses on sustainable farming practices and new technology to help farmers increase their maize and wheat yields.
Van Loon and his team design and produce machinery specifically suited for conditions in Mexico. That might mean adding fertilizer and seed bins to a 2-wheel tractor, modifying hand planters from China and Brazil or adapting a machine to be able to plant seeds for large or small grains. “This is going to be awesome,” Van Loon said while looking at a prototype of a shovel with seed and fertilizer boxes attached. One of the other tools his team is working with – a hand planter that deposits fertilizer and seed – was featured, along with Van Loon, in a Voice of America news article last month.
Van Loon, who came to CIMMYT in October 2012, has a background in agriculture and engineering and has worked throughout Latin America. Development is “in his blood,” he said, because his grandfather was a farmer and his parents worked in the Congo. He first came to Latin America as a teenager when he studied in Honduras as part of an exchange program. “I stayed a lot longer than I was supposed to,” said Van Loon, who also researched in Peru while working on his master’s degree. The chance to return to his “Latin roots” motivated Van Loon to apply for the smart mechanization position at CIMMYT. He said he has driven tractors since he was 10 years old and fixed motorcycles since he was 16, which helped him learn quickly on the job.
Many of the machines Van Loon and his team adapt are already used elsewhere in the world, but small changes or additions can make them more effective in Mexico or useful for multiple crops. By adding a water pump to a tractor, for example, or offering a variety of discs for a plow, machines can be more efficient. New tools are first designed using SolidWorks, a 3D modeling computer program. Implements are then stress-tested in the field to see how useful they are in local conditions. The team works with local blacksmiths so machines can be made and repaired in the area.
Throughout the process, Van Loon is in touch with the farmers who could benefit from his team’s work. “We see what they want to achieve and make it align with conservation agriculture principles,” he said. His team produces information sheets on the tools as well as plans that anyone can download and print, with the goal of making the innovations readily available. Van Loon said he spends about half of his time in the office and the other half in the field. MasAgro has hubs throughout Mexico, sometimes allowing him to ride his motorcycle nearly 1,700 kilometers to Ciudad Obregón, Sonora. He also explains his work to visitors, who can see the improved machines on display at a hangar at El Batán.
It takes collaboration to help farmers improve their maize and wheat yields, Van Loon said. His team is focused on the latter two-thirds of the “good seeds, good tools and good practices” equation farmers need to succeed. “We want to create a smart smallholder farmer,” Van Loon said.

 Innovations
Innovations 