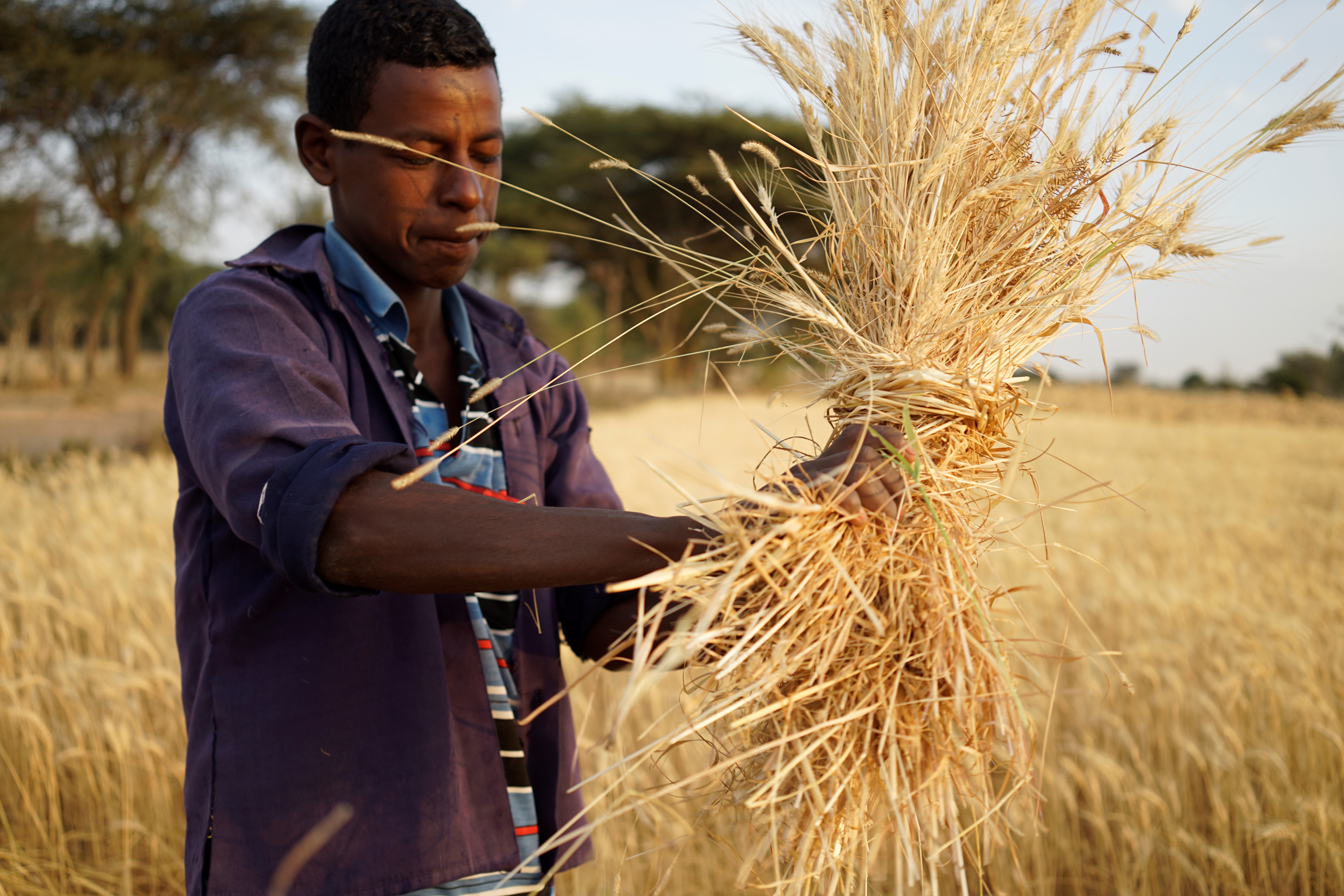
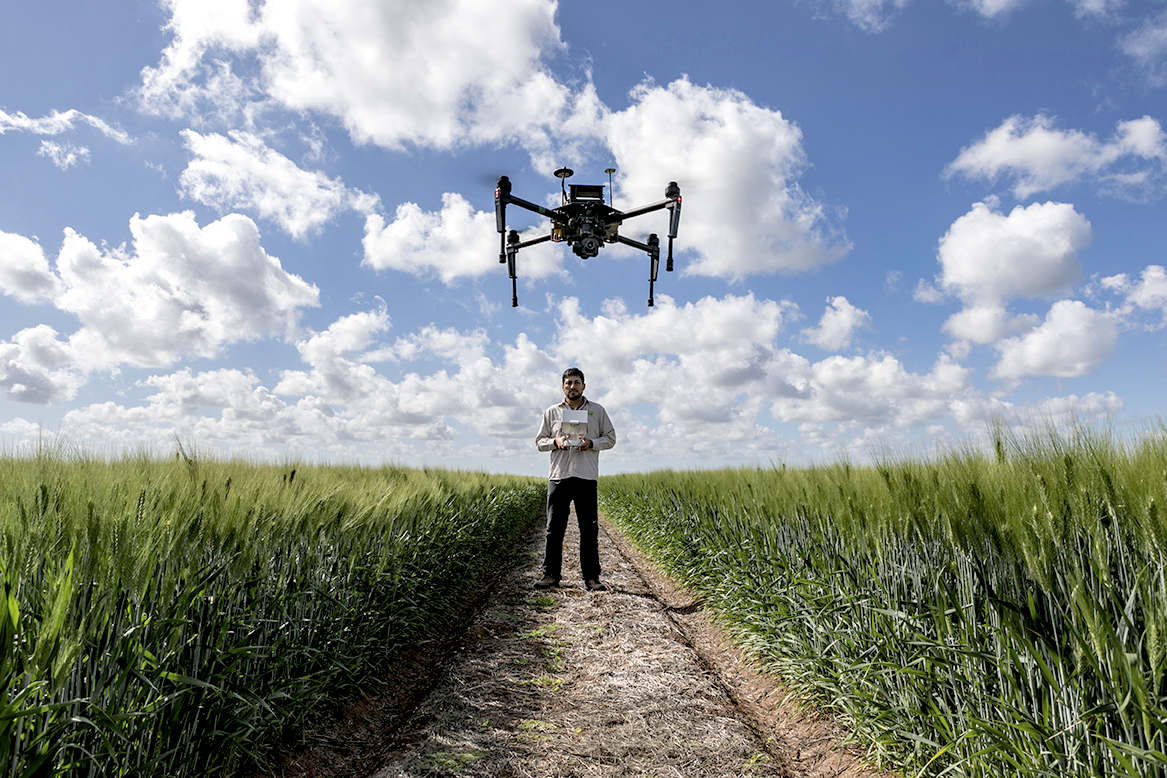
In crop research fields, drones and other high-tech sensing tools are now a common sight. They collect high-resolution data on a wide range of traits — from simple measurement of canopy temperature to complex 3D reconstruction of photosynthetic canopies.
This technological approach to collecting precise plant trait information, known as phenotyping, is becoming ubiquitous. According to experts at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and other research institutions, breeders can profit much more from these tools, when used judiciously.

In a new article in the journal Plant Science, CIMMYT Wheat Physiologist Matthew Reynolds and colleagues explain the different ways that phenotyping can assist breeding — from simple to use, “handy” approaches for large scale screening, to detailed physiological characterization of key traits to identify new parental sources — and why this methodology is crucial for crop improvement. The authors make the case for breeders to invest in phenotyping, particularly in light of the imperative to breed crops for warmer and harsher climates.
Read the full article:
Breeder friendly phenotyping.
This article was originally published on WHEAT.
Cover photo: Remote sensing specialist Francisco Pinto operates a UAV at CIMMYT’s research station in Ciudad Obregón, in Mexico’s Sonora state.


 Innovations
Innovations