Rapid urbanization, globalization, economic development, technological advancement, and changing agriculture production systems in South Asia are transforming food systems and the food environment.
India and Bangladesh, particularly, have seen a significant transformation since the advent of the Green Revolution as each became able to feed their population without having to import major crops.
However, that policy focus on food self-sufficiency and yield intensification has incurred significant health, environmental and fiscal costs, including a precipitous drop in crop diversification*.
This loss of crop diversification threatens economic and social development and environmental stability while weakening the crucial link between agriculture and community health, particularly in undernourished rural areas. To ensure sustainable food production and nutritional security, it is imperative to manage and conserve crop diversification.
To address these issues and ensure sustainable food production, there is an urgent need to transition from intensive to sustainable farming practices.
CIMMYT exploring crop diversification pathways
CIMMYT’s ongoing projects in South Asia, including the Transforming Agrifood Systems in South Asia (TAFSSA) and Transforming Smallholder Food Systems in the Eastern Gangetic Plains (RUPANTAR) are conducting extensive on-site and on-farm trials, including socioeconomic dimensions of farmers to promote crop diversification.
“To effectively address the challenges of crop diversification, it is essential to integrate on-farm trials and participatory action research, involving farmers in the experimentation and adaptation process tailored to their unique regional needs,” said Ravi Nandi, innovation systems scientist at CIMMYT in Bangladesh. “This hands-on involvement provides valuable data to guide policymaking, ensuring relevance and applicability.”
In addition, TAFSSA and RUPANTAR are engaging in participatory action research to uncover the most viable options for crop and livelihood diversification, understand the socioeconomic factors impacting farmers, and identify the potential opportunities and challenges associated with the crop and livelihood diversification efforts among the farmers.
Researchers completed two comprehensive surveys, engaging with 2,500 farmers across the Eastern Gangetic Plains (EGP) of India, Nepal and Bangladesh, yielding valuable data that will inform future strategies for crop diversification in the region.
Ongoing investigations into the political economy of policies for crop diversification in Bangladesh generate novel insights, further contributing to the development of efficient crop diversification projects and sustainable agricultural policies.
The rise of crop diversification in practices and policy
In recent years, crop diversification has gained traction as a promising strategy to boost agricultural productivity, reduce risks (production, market, climate, and environmental), enhance nutritional outcomes, and promote sustainable agriculture.
Following the inaugural National Conference of Chief Secretaries in Dharamshala, India, led by the Prime Minister of India, state governments introduced numerous policies and schemes to support crop diversification. Some of these initiatives, highlighted in Figure 1, were backed by substantial budget allocations aimed at motivating farmers to diversify their crop production from the current intensive production system.
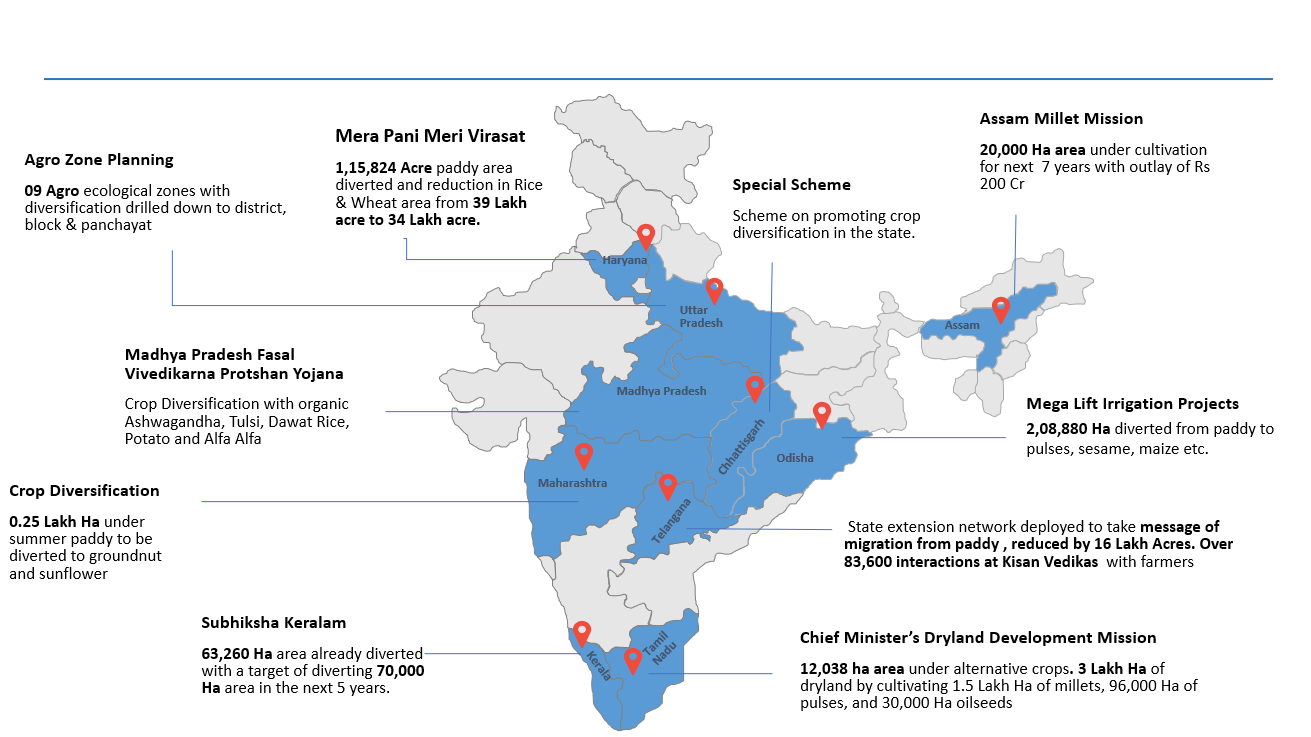
Similar initiatives have been started in Bangladesh, Nepal and other South Asian countries to promote crop diversification. These policies and schemes are important steps towards addressing inadequacies that intensive farming has created in agriculture and food systems.
While policies promoting crop diversification in South Asia are a positive step, their effectiveness is contingent on evidence-based decision-making. The complexities of implementing diversification strategies vary significantly depending on local contexts, particularly in countries like India, Nepal and Bangladesh, where most farmers operate on less than one hectare of land and face diverse weather conditions.
Smallholder farmers, at risk of losing economic stability from abandoning profitable monocrops, face additional challenges because of limited access to advanced technologies and fragmented markets, making the transition to diversified farming a precarious endeavor.
A shift towards comprehensive multi-criteria assessments, including qualitative methods and stakeholder interactions, is necessary for creating practical and locally relevant indicators. Supporting infrastructure, accessible extension services and market development, along with empowering farmers through education on agronomic practices and crop management, will play a crucial role in successfully implementing and reaping the benefits of crop diversification.
*Crop diversification is a process that makes a simplified cropping systems more diverse in time and space by adding additional crops.

 Climate adaptation and mitigation
Climate adaptation and mitigation 
