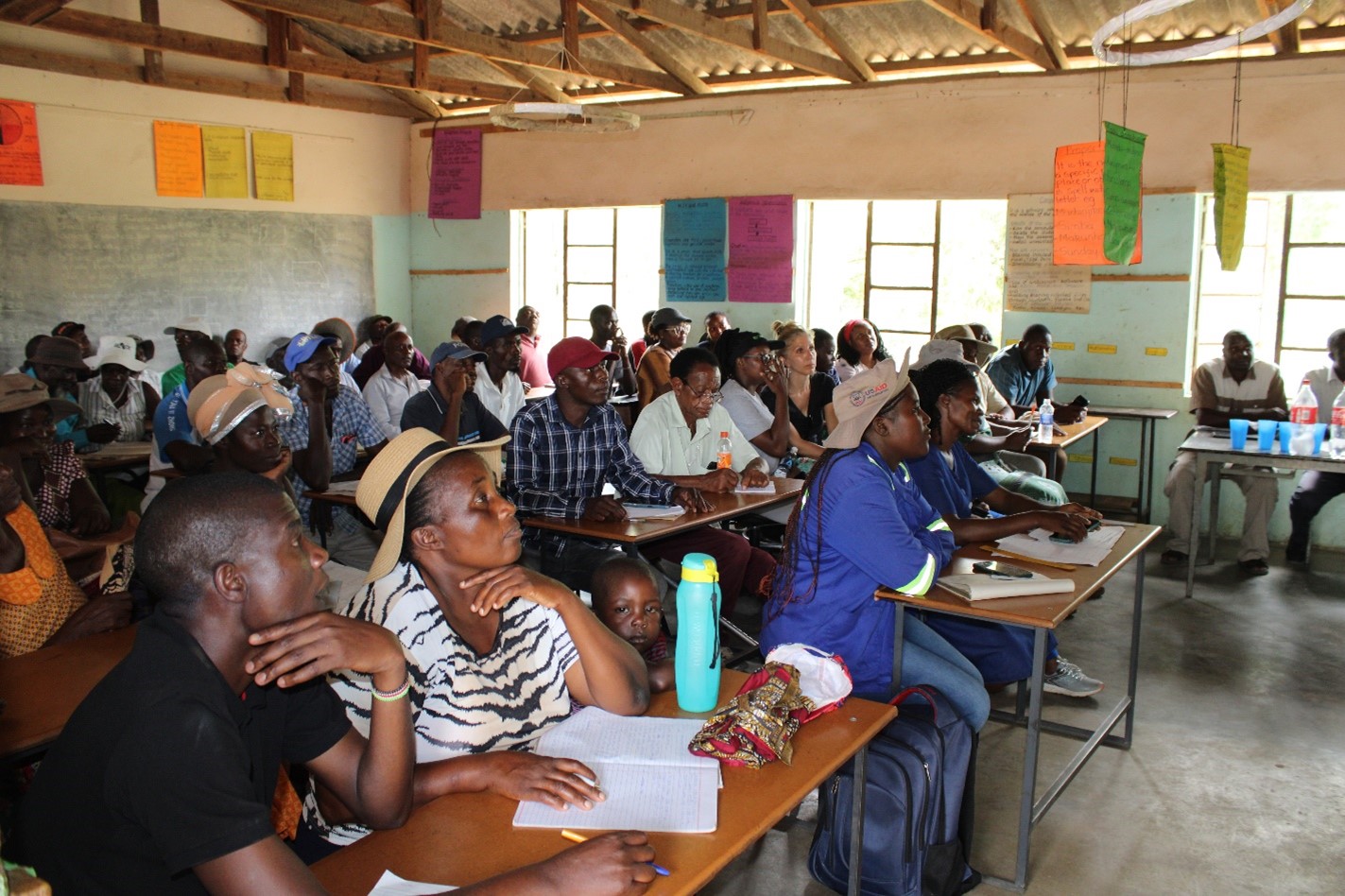

In the rural districts of Mbire and Murehwa in Zimbabwe, the CGIAR Agroecology Initiative (AE-I) has embarked on a comprehensive strategy that places farmers’ opinions at the heart of interventions to tackle the multifaceted challenges of agroecosystems. Recognizing challenges such as pest and disease outbreaks, periodic drought, inadequate grazing lands, and limited access to quality seeds and livestock breeds, the AE-I team has initiated a collaborative process involving various stakeholders to develop tailored agroecological solutions.
This integrated approach emphasizes active participation and cooperation among agricultural extension services, including the Department of Agricultural Technical and Extension Services of Zimbabwe (AGRITEX), food system actors (FSAs), and technology providers. These organizations have collaborated to form Agroecology Living Landscapes (ALLs) to identify, test, and iterate relevant innovations.
“This collaborative innovation and ongoing co-designing cycle empower local communities and fosters agricultural sustainability, positioning Zimbabwe as a model for agroecology transition,” said Vimbayi Chimonyo, CIMMYT scientist and crop modeler. “With these efforts, the AE-I is improving current agricultural practices but also building a foundation for future resilience in Zimbabwe’s rural districts.”
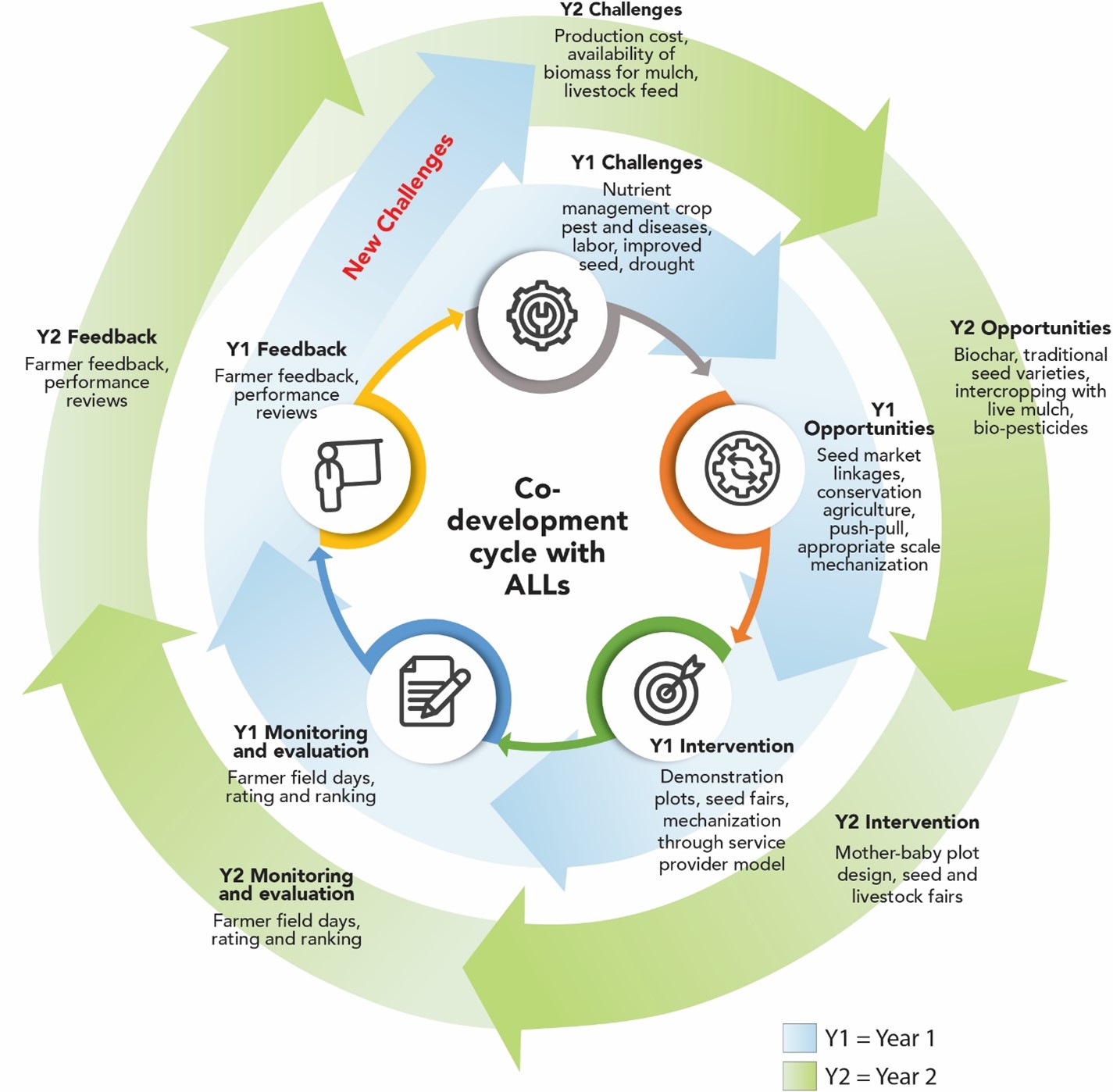
To ensure a well-informed process, the AE-I research team began its efforts by identifying dominant value chains in the two districts. In Murehwa, these included horticulture, maize, groundnuts, and poultry; while in Mbire, sorghum, cotton, and livestock. Challenges noted included production constraints (availability of improved seed and labor), biophysical constraints (water availability, increased incidents of fall armyworm), economic (market access) and social (agency).
Next, the AE-I research team, and the ALLs conducted a series of surveys, focus group discussions, and key informant interviews to understand existing opportunities that might address the challenges and aid in strengthening the value chains. The AE-I team discovered opportunities related to addressing labor shortages and improving access to improved technologies.
As a result, the research team introduced appropriate scale machinery, suggested seed and livestock fairs to increase access to agroecological inputs, established a series of demonstration plots to showcase technologies that improve water use, and increased mitigation efforts for fall armyworm. After introducing machinery, seed and livestock fairs, and testing the technologies during the 2022/23 season, AE-I returned to ALL members to discuss the impact the activities had on their production systems and determine if any modifications were necessary.
Participants suggested increased visibility of the new technologies and methods, so the AE-I team enhanced demonstration plots and added 100 baby plots during the 2023-24 farming season.
Integrating adaptive testing and feedback yielded valuable information from farmers, providing a strong base for further adaptations in the 2023-24 farming season. This continuous engagement promoted adaptive and context-specific solutions within the AE-I, ensuring that interventions aligned with evolving community needs.
Technologies being tested
To achieve the visions of each ALL, context-specific technologies are being tested to ensure synergy across the identified value chains and collaboration among different food system actors.
| Technology/Innovation | Description |
| Demo plots | 2022-23: Twenty mother plots were established to compare the performance of cereal planted in, push-pull, and conventional practices on productivity, rainwater use efficiency, and pest biocontrol.
2023-24: Additional treatments, including biochar, live mulch, and traditional treatments, were introduced. One hundred eleven baby plots were established where farmers adapted mother protocols to suit their contexts. |
| Farmer Field Days | Conducted for the established demonstration plots in Mbire and Murehwa, these field days showcased the technologies to a broader audience and acted as an agent of evaluation and feedback for the AE-I team. |
| Mechanization | A service provider model was adopted to introduce appropriate scale machinery, addressing the drudgery associated with farming operations. Equipment provided included threshers, basin diggers, two-wheel tractors, rippers, mowers, chopper grinders, and balers. Training on operation, repair, and maintenance was also provided. |
| Capacity building | Yearly work plans, co-designed by ALLs, identification of training needs, gaps, and priorities. Facilitated by AGRITEX, these trainings equip farmers with knowledge essential to facilitate agroecology transition and fulfil ALL visions. |
Monitoring and evaluation is a valuable component in the co-designing process where the AE-I establishes a feedback loop, engaging farmers and government stakeholders in participatory monitoring and evaluation. This ongoing exercise analyzes various indicators across different experimental treatments, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness and suitability of these approaches within the agricultural context. This continuous analysis leads to further co-designing of tailored solutions for facilitating the agroecology transition.
Farmers and stakeholders from AGRITEX welcomed and appreciated the co-designing process, as they felt empowered by the entire process. They expressed how it gives them ownership of the technologies being implemented through the AE-I project.
The success of the AE-I in the Mbire and Murehwa districts hinges on active participation and collaboration among FSAs. By continuously evaluating and integrating feedback on innovations and addressing challenges through context-specific interventions, the initiative is paving the way for adopting agroecological practices in farming, enhancing the resilience of local food systems.
This original piece was written by Craig E. Murazhi, Telma Sibanda, Dorcas Matangi, and Vimbayi G. P. Chimonyo.

 Capacity development
Capacity development