In conflict-ridden Sudan, Gadarif State in Eastern Sudan is the most important region for sorghum production, with about 5-6 million feddan (5.18-6.22 acres) cultivated on an annual basis on large scale farms equipped with agricultural machinery. However, like the country, the state is covered with vertisols, clay-rich soils that shrink and swell with changes in moisture content, that become waterlogged and cannot be properly cultivated during rainy season.
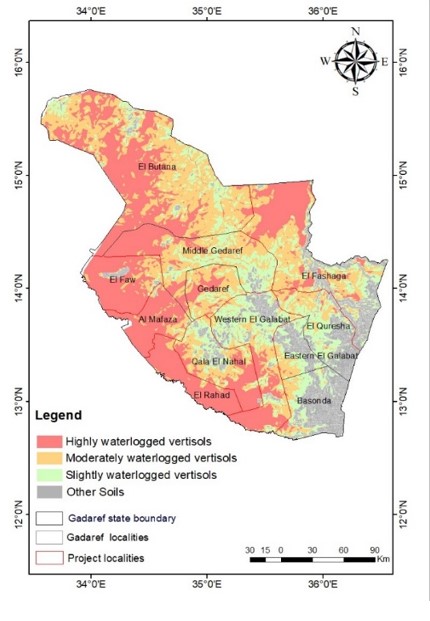
To address the issue, technical experts from the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) are mapping areas affected by waterlogging in two localities, namely El Fashaga and El Nahal, to identify the most suitable lands to establish large drainage implementing sites integrated with improved crop varieties of sorghum. This work is part of CIMMYT’s Sustainable Agrifood Systems Approach for Sudan (SASAS) program, which works with farmers and herders to reduce their need for humanitarian assistance in conflict-affected Sudan.
“To address the issue of vertisols affected by water logging in Al Gadarif, the prominent agricultural region in Sudan, we used the map developed by ICRISAT in 2023 and consulted with local farmers to identify 100 hectares El Fashaga and El Nahal localities to improve drainage and avoid waterlogging,” said Gizaw Desta, senior scientist at ICRISAT.
Waterlogging is common on poorly drained soil or when heavy soil is compacted, preventing water from being drained away. This leaves no air spaces in the saturated soil, and plant roots literally drown. Waterlogging can be a major constraint to plant growth and production and, under certain conditions, will cause plant death. In Gadarif state, 2.3 million hectares and 1.8 million hectares of vertisols are under high and moderate waterlogging conditions that impair crop production during the rainy season, leading to food insecurity if not reversed with appropriate agricultural practices.
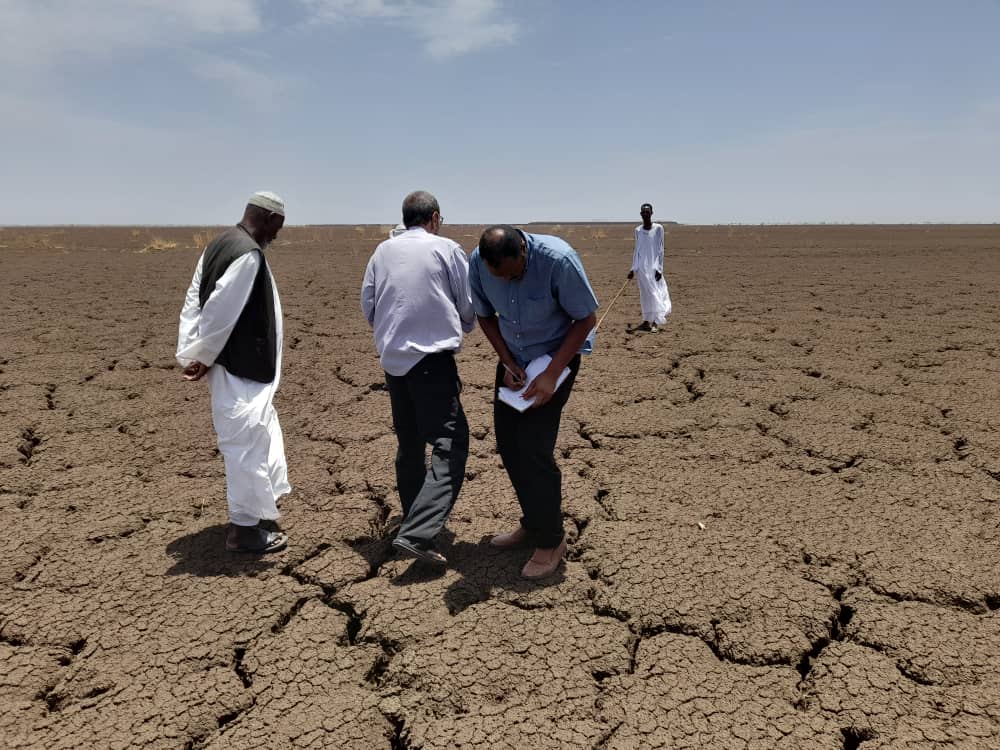

“For years, my farm has been flooded by water during the rainy season, and I cannot cultivate sorghum as plants die of water suffocation”, said Ali Ahmed, a farmer from Al-Saeeda area of Al-Nahal locality who is affected by waterlogging. “Alternatively, we as farmers affected by waterlogging were forced to cultivate watermelon instead of our main staple food sorghum. This shift in the crops we cultivate is hardly affecting our income. I am glad that ICRISAT is working to establish drainage systems and address waterlogging within our lands.”
“At SASAS, we strive to ensure that farmers have access to fertile lands and other agricultural inputs. We work with our partners to address all problems facing farmers including waterlogging to help farmers continue producing their staple food and cash crops,” said Abdelrahman Kheir, SASAS chief of party in Sudan.

 Capacity development
Capacity development 
