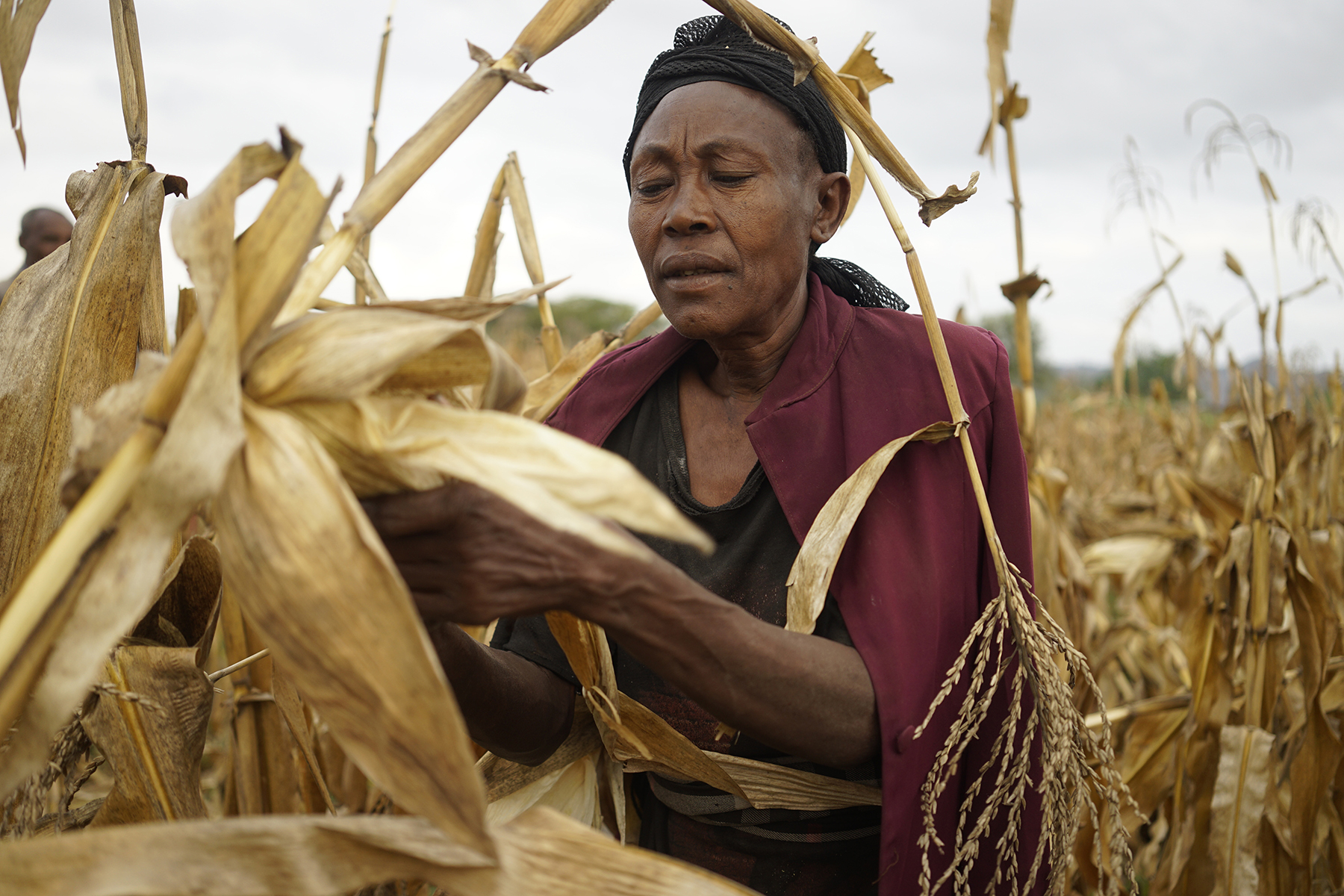

EL BATAN, Mexico (CIMMYT) – El Niño drought-related stress is triggering hunger and food insecurity that will endanger food security for 40 million people in southern Africa, according to the World Food Programme. While not as tangible as humanitarian aid, long-term scientific research is key to addressing the major drought threatening parts of Central America, Africa and Asia. Government fiscal tightening makes it hard to defend investments in research against projects where the results may be immediate and obvious – but long-term investment equals long-term impact.
Reduced harvests due to drought
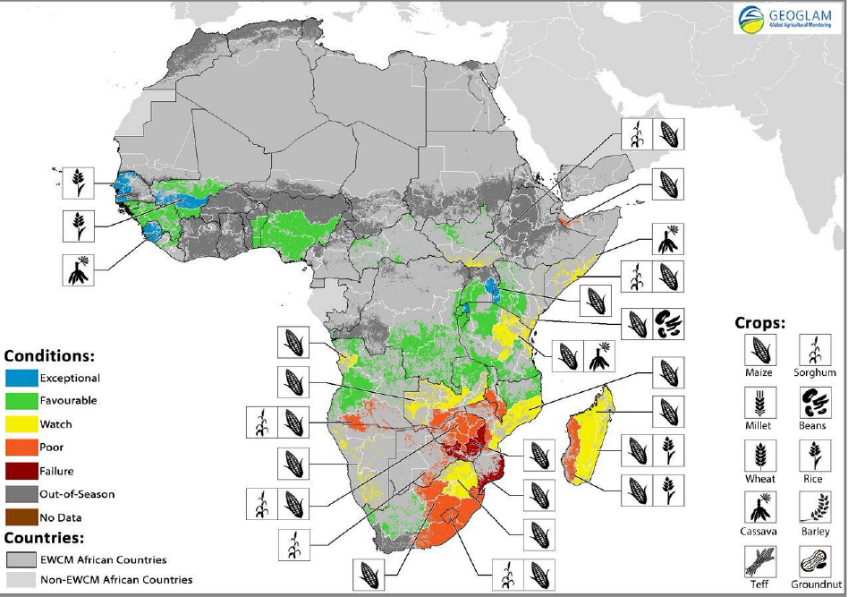
South Africa, which is normally a regional exporter, will need to import 5 to 6 million tons of maize to mitigate the widespread crop failure. As the continent’s largest maize producer this is having a knock on effect on the region. Zimbabwe, which depends on food imports from South Africa, declared a state of disaster last month, due to drought. Malawi and Mozambique have also experienced soaring food prices. Millions in the region will need food assistance, which means massive imports. In much of southern Africa, 30 – 50 day delays in the onset of rains has caused curtailed planting, setting the scene for widespread crop failure.
Ethiopia is experiencing the worst drought in decades, with more people requiring food assistance in 2016 than at any point since 2005, according to the Famine Early Warning Systems Network. In the central and eastern part of the countries crop production is down by 25 to 70% after the lowest rains in more than 50 years.
The El Niño related drought is not limited to Africa. India is set to harvest its smallest wheat crop in six years, with production down by five percent, following two successive poor monsoon seasons. But the biggest concern is that the region could experience major drought episodes like the Horn of Africa drought 1981- 1984 and the South Africa drought 1992, causing massive social disruption and human suffering.
Drought tolerant crops are an insurance against hunger and crop failure.
Given the severity of drought, scientific researchers are faced with the challenge to devise seed and farming practices that offer farmers greater resilience under this stress. Ongoing work to develop drought tolerant varieties has proved successful but needs renewed support and expansion.
Various maize landraces and wild relatives of wheat have withstood harsh conditions for thousands of years. Exploiting the drought-tolerances they possess and involving the use of molecular markers to better understand the genetic basis of drought tolerance has helped breeders select for better drought tolerance. This is not a quick fix. It can cost up to $600,000 and take seven years to produce a single maize hybrid. Hybrids tend to be more drought tolerant because they are more robust, implying deeper roots that allows the plant to capture more water.
CIMMYT is working with national partners in Ethiopia to rapidly get drought tolerant maize and wheat seed to farmers as part of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) funded Emergency Seed Response in Ethiopia project. The USAID and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation funded Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa project has brought 184 distinct varieties to farmers, mostly hybrids that yield on average 49% more grain than open-pollinated varieties, and yield higher than or equal to currently available varieties on the market.
A single seed can make the difference between hunger and prosperity, but seed alone is not enough. Imagine a Ferrari that is designed to travel at high speed on a freshly paved highway, driving along a dirt road. It will either break down or drive badly. The same thing happens with seed that is planted without smart farming practices designed to increase efficiency. There are many factors that need to be considered, including: right planting date, water conserving tillage methods, and fertilizer. If you can establish the plant well, it is more likely to perform well when drought stress really hits.
Plant a seed today
Massive investments are required today in order for farmers to benefit from effective technologies in the future given that benefits from agricultural research tend to come to fruition after a considerable time lag. Today, parts of Central America, Africa and Asia desperately need food assistance – but the need for investment in agricultural research for development will only intensify as more countries face drought and other climate-related stress. As the proverb asks: “When is the best time to plant a tree?” Twenty years ago. “The second-best time?” Today.
 Climate adaptation and mitigation
Climate adaptation and mitigation