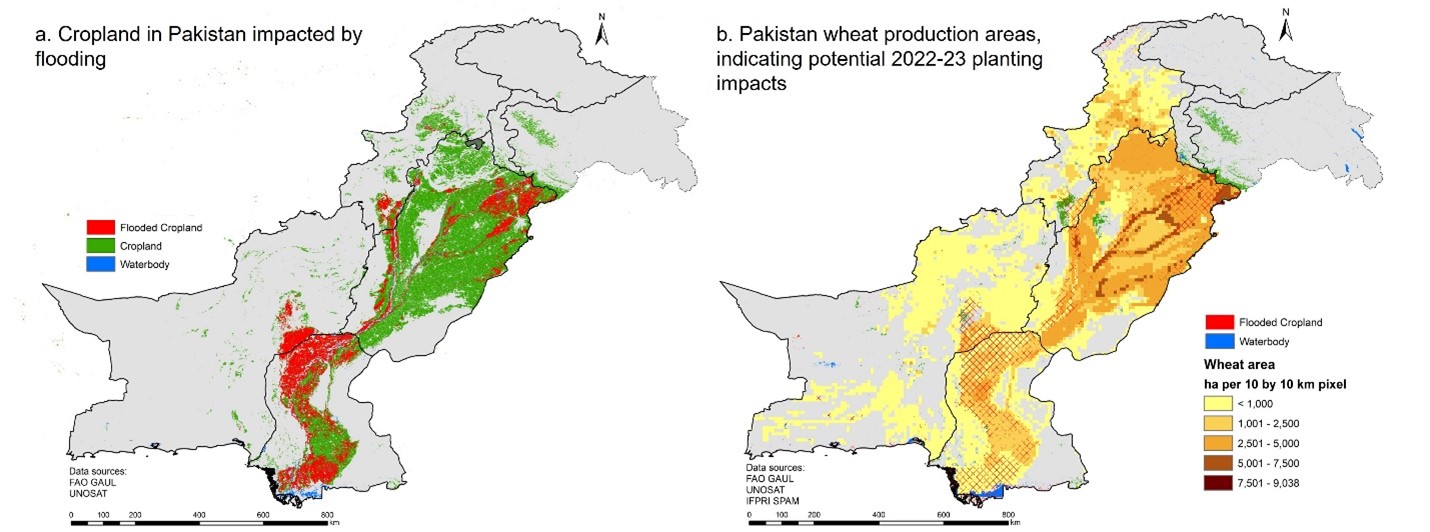
Heavy summer rains have led to severe floods in Pakistan, affecting over 800,000 hectares of land. Rural areas in the southern coastal provinces have been hardest hit with water levels remaining high throughout the Indus River system. This compounds the existing inequalities in livelihoods and represents significant humanitarian as well as agricultural impacts.
Due to flood damage, the estimated direct crop loss by economists stands at around $2.3 billion. Reports indicate that over 32 million people have been displaced by the flooding and urgent humanitarian needs include access to food, water, shelter, and public health.
The International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) strongly encourages enhanced investment in ensuring that our agricultural systems can adapt to as well as mitigate climate change impacts. In the current context, the development and distribution of improved wheat seed must be seen as a central pillar of flood response to secure wheat-dependent livelihoods.
No single drop, be it geo-political or climatic, will tip the balance on our global food system. But we must be increasingly aware of the compounding and amplifying effects of each crisis and develop strategies towards more sustainable agri-food systems.
Read the full study: One drop at a time: recent heavy rain has led to flooding in Pakistan, devastating agricultural land, and rural communities
Cover photo: Current areas of cropland and flood-affected crop land in Pakistan. This highlights the significant impacts of the flood waters, particularly on cropland in southern parts of the country. The boundaries shown on this map do not imply official endorsement or acceptance.

 Climate adaptation and mitigation
Climate adaptation and mitigation 
