Many maize farmers in sub-Saharan Africa grow old varieties that do not cope well under drought conditions. In the Oromia region of Ethiopia, farmer Sequare Regassa is improving her family’s life by growing the newer drought-tolerant maize variety BH661. This hybrid was developed by the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR), using CIMMYT’s drought-tolerant inbred lines and one of EIAR’s lines. It was then officially released in 2011 by the EIAR as part of the Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (DTMA) project, funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and continued under the Stress Tolerant Maize for Africa (STMA) initiative.
“Getting a good maize harvest every year, even when it does not rain much, is important for my family’s welfare,” said Regassa, a widow and mother of four, while feeding her granddaughter with white injera, a flat spongy bread made of white grain maize.
Since her husband died, Regassa has been the only breadwinner. Her children have grown up and established their own families, but the whole extended family makes a living from their eight-hectare farm in Guba Sayo district.

On the two hectares Regassa cultivates on her own, she rotates maize with pepper, sweet potato and anchote, a local tuber similar to cassava. Like many farming families in the region, she grows maize mainly for household food consumption, prepared as bread, soup, porridge and snacks.
Maize represents a third of cereals grown in Ethiopia. It is cheaper than wheat or teff — a traditional millet grain — and in poor households it can be mixed with teff to make the national staple, injera.
In April, as Regassa was preparing the land for the next cropping season, she wondered if rains would be good this year, as the rainy season was coming later than usual.
In this situation, choice of maize variety is crucial.
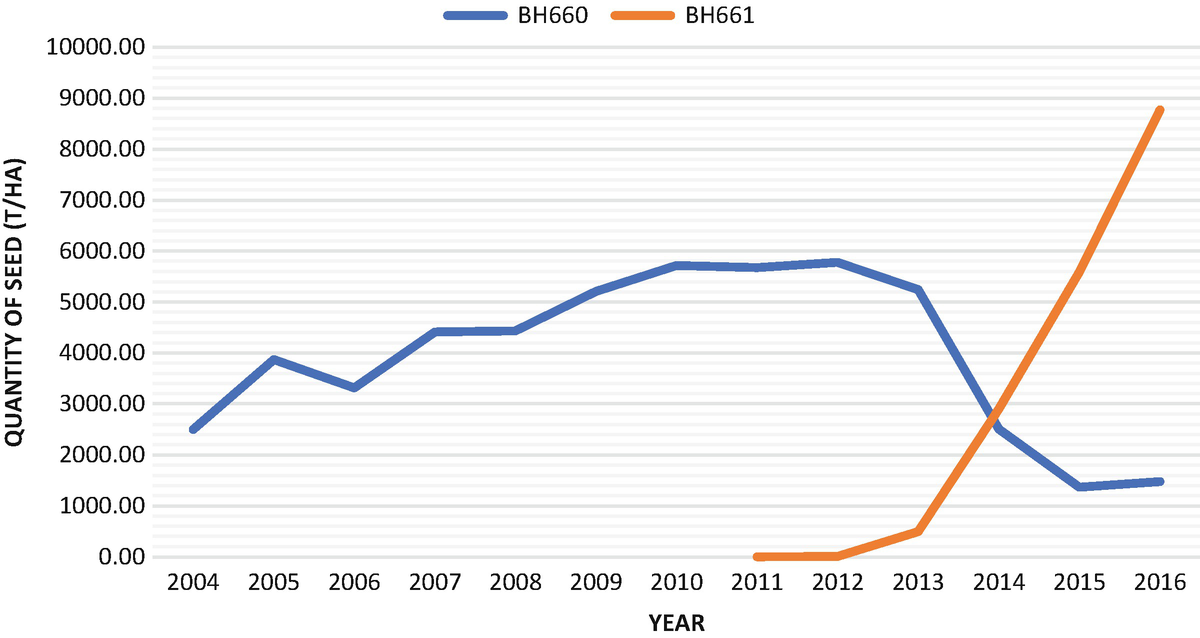
She used to plant a late-maturing hybrid released more than 25 years ago, BH660, the most popular variety in the early 2000s. However, this variety was not selected for drought tolerance. Ethiopian farmers face increasing drought risks which severely impact crop production, like the 2015 El Nino dry spell, leading to food insecurity and grain price volatility.

Laborious development for fast-track adoption
Under the DTMA project, maize breeders from CIMMYT and the Ethiopian Institute for Agricultural Research (EIAR) developed promising drought-tolerant hybrids which perform well under drought and normal conditions. After a series of evaluations, BH661 emerged as the best candidate with 10% better on-farm grain yield, higher biomass production, shorter maturity and 34% reduction in lodging, compared to BH660.
The resulting BH661 variety was released in 2011 for commercial cultivation in the mid-altitude sub-humid and transition highlands.
The year after, as farmers experienced drought, the Ethiopian extension service organized BH661 on-farm demonstrations, while breeders from CIMMYT and EIAR organized participatory varietal selection trials. Farmers were impressed by the outstanding performances of BH661 during these demos and trials and asked for seeds right away.
Seed companies had to quickly scale up certified seed production of BH661. The STMA project team assisted local seed companies in this process, through trainings and varietal trials. Companies decided to replace the old hybrid, BH660.
“In addition to drought tolerance, BH661 is more resistant to important maize diseases like Turcicum leaf blight and grey leaf spot,” explained Dagne Wegary, a maize breeder at CIMMYT. “For seed companies, there is no change in the way the hybrid is produced compared to BH660, but seed production of BH661 is much more cost-effective.”
EIAR’s Bako National Maize Research Center supplied breeder seeds to several certified seed producers: Amhara Seed Enterprise (ASE), Bako Agricultural Research Center (BARC), Ethiopian Seed Enterprise (ESE), Oromia Seed Enterprise (OSE) and South Seed Enterprise (SSE). Certified seeds were then distributed through seed companies, agricultural offices and non-governmental organizations, with the technical and extension support of research centers.

From drought risk to clean water
After witnessing the performance of BH661 in a neighbor’s field, Regassa asked advice from her local extension officer and decided to use it. She is now able to produce between 11-12 tons per hectare. She said her family life has changed forever since she started planting BH661.
With higher maize grain harvest, she is now able to better feed her chickens, sheep and cattle. She also sells some surplus at the local market and uses the income for her family’s needs.
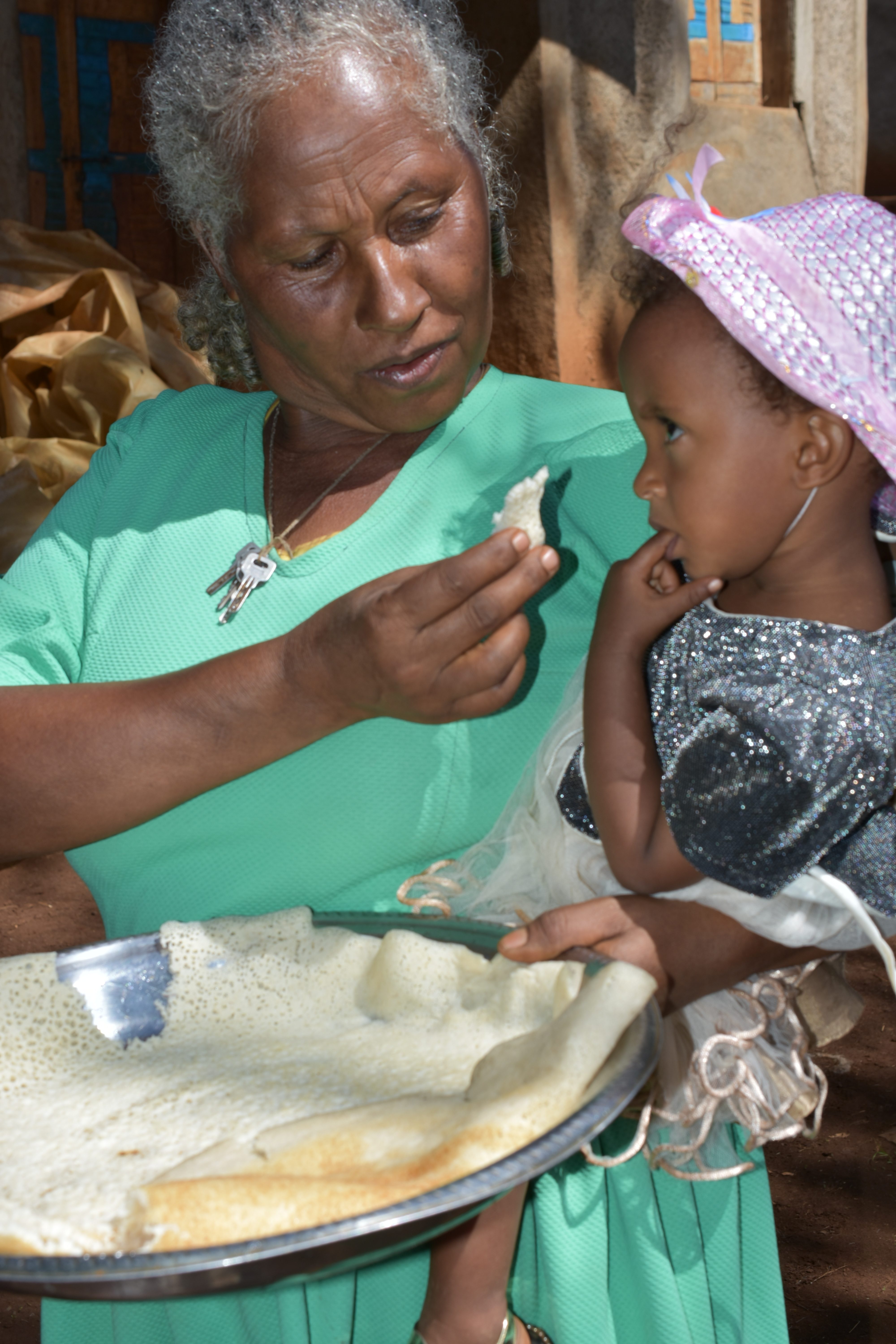

“If farmers follow the recommended fertilizer application and other farming practices, BH661 performs much better than the old BH660 variety,” explained Regassa. “If we experience a drought, it may be not that bad thanks to BH661’s drought tolerance.”
Regassa buys her improved seeds from the Bako Research Station, as well as from farmers’ cooperative unions. These cooperatives access seeds from seed companies and sell to farmers in their respective districts. “Many around me are interested in growing BH661. Sometimes we may get less seeds than requested as the demand exceeds the supply,” Regassa said.
She observed that maize prices have increased in recent years. A 100 kg bag of maize that used to sell for 200–400 Ethiopian birr (about $7–14) now sells for 600–700 Ethiopian birr (about $20–23). With the increased farmers’ wealth in her village, families were able to pay collectively for the installation of a communal water point to get easy access to clean water.
“Like women’s role in society, no one can forget the role maize has in our community. It feeds us, it feeds our animals, and cobs are used as fuel. A successful maize harvest every year is a boon for our village,” Regassa concluded.

 Climate adaptation and mitigation
Climate adaptation and mitigation